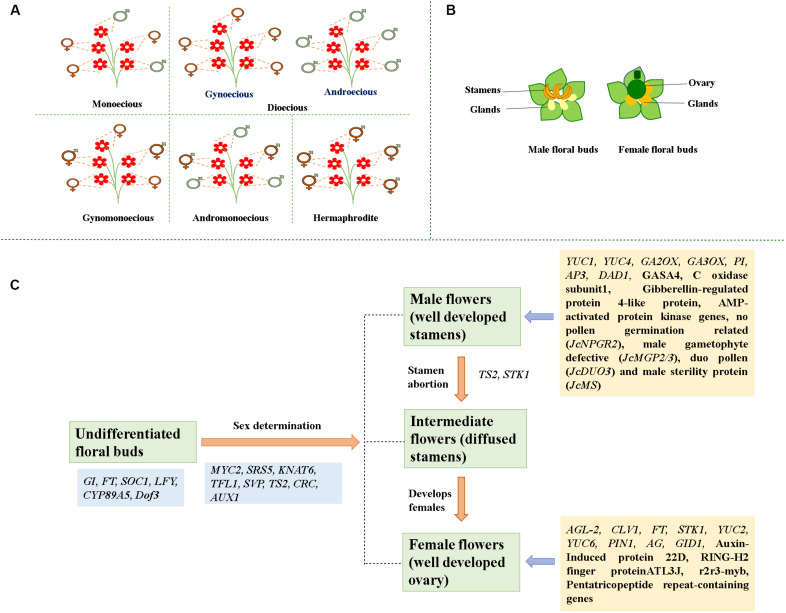
FIGURE 1.
(A) Diversified morphology of flowers.  Represents male flowers;
Represents male flowers;  Represents female flowers;
Represents female flowers;  Represents hermaphrodite flowers. (B) Morphology of male and female floral buds in Jatropha.
(C) Key genes involved in the floral transition, sex determination, and reproductive organ development (GI-GIGANTEA; FT-FLOWERING LOCUS T; SOC1-SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1; LFY-LEAFY; CYP89A5-CYTOCHROME P450; SRS5-SHI-RELATED SEQUENCE 5; KNAT6-KNOTTED1-LIKE HOMEOBOX GENE 6; TFL1-TERMINAL FLOWER 1; SVP-SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE; TS2-TASSELSEED2; CRC-CRABS CLAW; AUX1-Auxin transporter protein 1; STK1-SEEDSTICK; YUC1-Flavin-containing monooxygenase; YUC2/4/6-Indole-3-pyruvate monooxygenase; GA3ox-Gibberellin 3-beta-hydroxylase; GA20ox-Gibberellin 20-oxidase; PI-PISTILLATA; AP3-APETALA3; DAD1-DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCENCE 1; GASA4-Gibberellin-regulated protein 4 precursor; AGL2-AGAMOUS-LIKE 2; CLV1-CALVATA1; PIN1-PIN-FORMED 1; AG2-AGAMOUS-like protein 2; GID1-Gibberellin receptor protein).
Represents hermaphrodite flowers. (B) Morphology of male and female floral buds in Jatropha.
(C) Key genes involved in the floral transition, sex determination, and reproductive organ development (GI-GIGANTEA; FT-FLOWERING LOCUS T; SOC1-SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1; LFY-LEAFY; CYP89A5-CYTOCHROME P450; SRS5-SHI-RELATED SEQUENCE 5; KNAT6-KNOTTED1-LIKE HOMEOBOX GENE 6; TFL1-TERMINAL FLOWER 1; SVP-SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE; TS2-TASSELSEED2; CRC-CRABS CLAW; AUX1-Auxin transporter protein 1; STK1-SEEDSTICK; YUC1-Flavin-containing monooxygenase; YUC2/4/6-Indole-3-pyruvate monooxygenase; GA3ox-Gibberellin 3-beta-hydroxylase; GA20ox-Gibberellin 20-oxidase; PI-PISTILLATA; AP3-APETALA3; DAD1-DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCENCE 1; GASA4-Gibberellin-regulated protein 4 precursor; AGL2-AGAMOUS-LIKE 2; CLV1-CALVATA1; PIN1-PIN-FORMED 1; AG2-AGAMOUS-like protein 2; GID1-Gibberellin receptor protein).