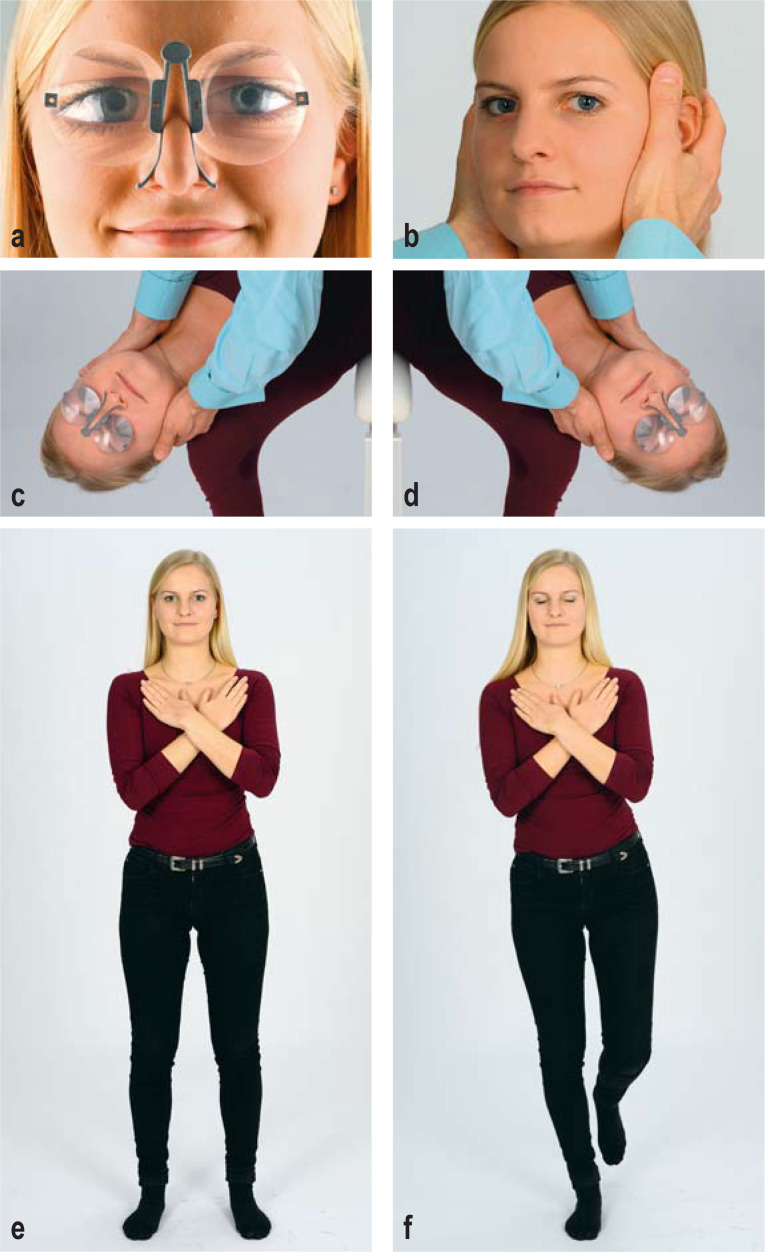
Figure 2.
The clinical examination of a patient complaining of vertigo, dizziness, or postural imbalance.
a) Inspection for spontaneous nystagmus. This should be performed with and without fixation, with the aid of Frenzel goggles (M glasses, illustrated).
b) Clinical head-impulse test. The examiner should look for possible refixation saccades, which indicate dysfunction of the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR).
c, d) All patients, regardless of their history, should be investigated for positional vertigo with rotation of the head by 45° and simultaneous positioning in the opposite direction. Diagnostic positioning maneuvers (SémontPlus) are shown for c) the right posterior semicircular canal and d) the left posterior semicircular canal.
e, f) Romberg test: e) basic test condition with the legs apart and the eyes open; f) advanced test condition with the patient standing on one leg and keeping both eyes closed.