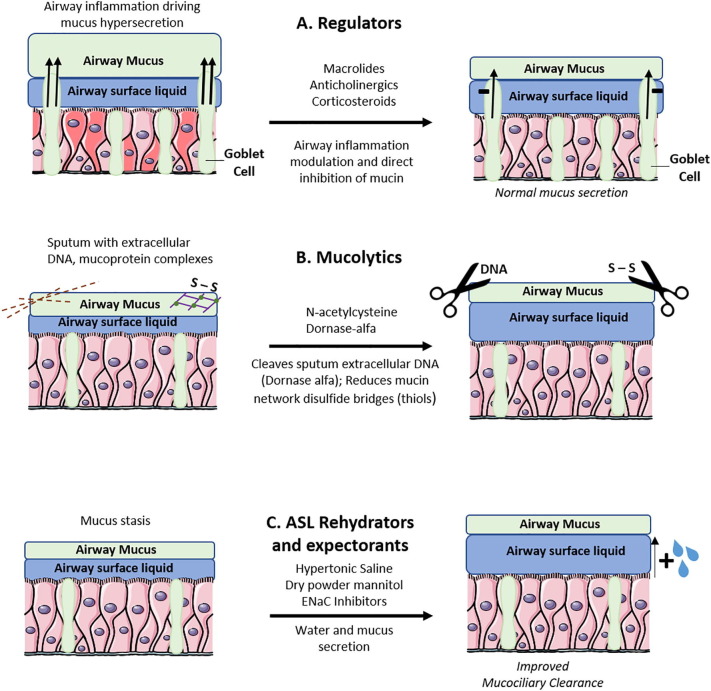
Fig. 1.
(A) Regulators of goblet cell mucus secretion. Anticholinergics decrease mucus secretion by inhibition of neutrophil elastase driven mucin production (11). Anti-inflammatory agents such as corticosteroids and macrolides decrease mucus hypersecretion in airway inflammation. (B) Mucolytic agents break down mucus network structures to favorable biophysical properties for improved mucociliary clearance. Dornase-alfa hydrolyzes extracellular DNA in sputum and N-acetylcysteine reduces disulfide bonds in mucus networks. (C) Airway surface liquid (ASL) rehydrators reverse ASL height reduction to improve mucociliary clearance. These also increase mucus secretion as expectorators hypertonic saline and dry powder mannitol rehydrate ASL by hyperosmolar action. Epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) inhibitors prevent ASL depletion by hyperabsorption of sodium and water through ENaC.