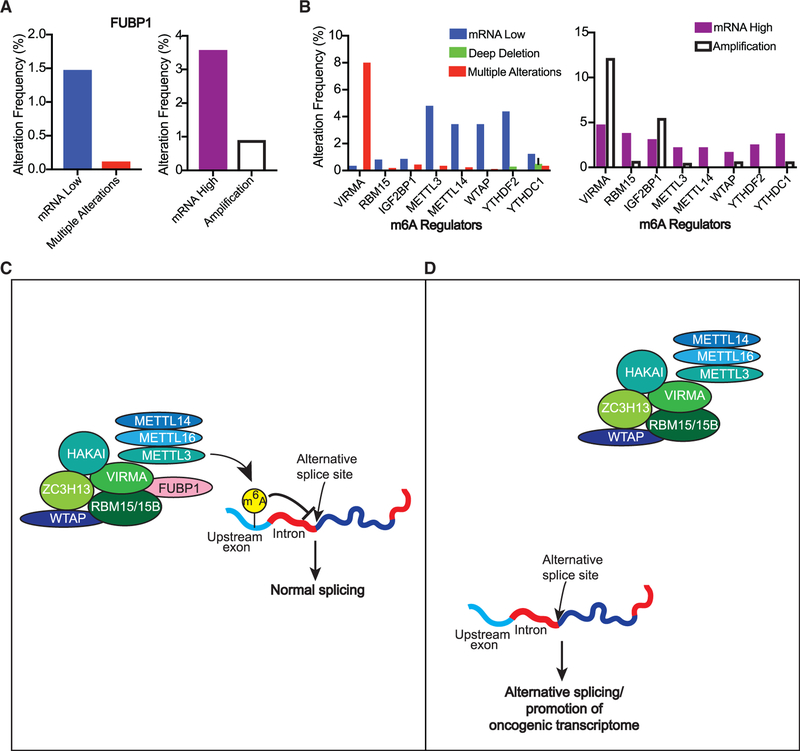
Figure 5. FUBP1 and Other m6A-Associated Proteins that Are Altered in Human Breast Cancers.
(A and B) Percentage of breast cancer samples with (A) low (left) or high (right) copy number or mRNA alterations in FUBP1 or (B) other m6A-related genes, reported by METABRIC (2,509 samples).
(C and D) Schematic representation of FUBP1 mechanism in regulating alternative splicing: FUBP1 binds VIRMA and RBM15 to help recruit the rest of the m6A complex to target mRNA sites that affect splicing of cancer drivers (C). In the context of FUBP1 loss (D), there are fewer m6A modifications, thus preventing the interaction of normal m6A-binding proteins with modified sites and their downstream effects, i.e., AS of cancer driver genes.