Author response image 1. Behavioral correlates of stimulus-locked pupil responses in yes/no tasks.
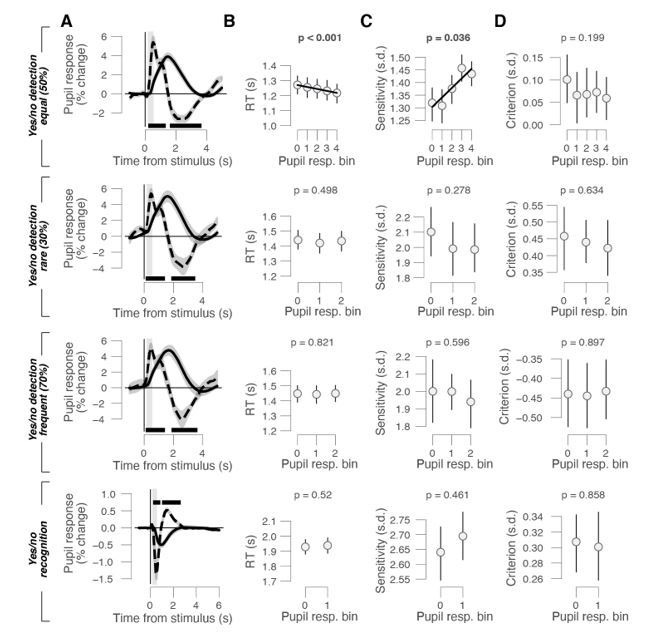
(A) Task-evoked pupil response (solid line) and response derivative (dashed line) aligned to stimulus onset in the yes/no detection datasets with equal, rare, and frequent signals and the yes/no recognition dataset, respectively. Grey window, interval for task-evoked pupil response measures (range, 0.23-0.5 s); black bar, significant pupil derivative; stats, cluster-corrected one-sample t-test. (B) Relationship between RT and task-evoked pupil response. Linear fits were plotted if first-order fit was superior to constant fit; quadratic fits were not superior to first-order fits. Stats, mixed linear modeling (detection data sets), or paired-samples t-test (recognition data set). (C) As B, but for perceptual sensitivity. (D) As B, but for choice bias. All panels: group average (N = 24; N = 15; N = 15; N = 54); shading or error bars, s.e.m.
