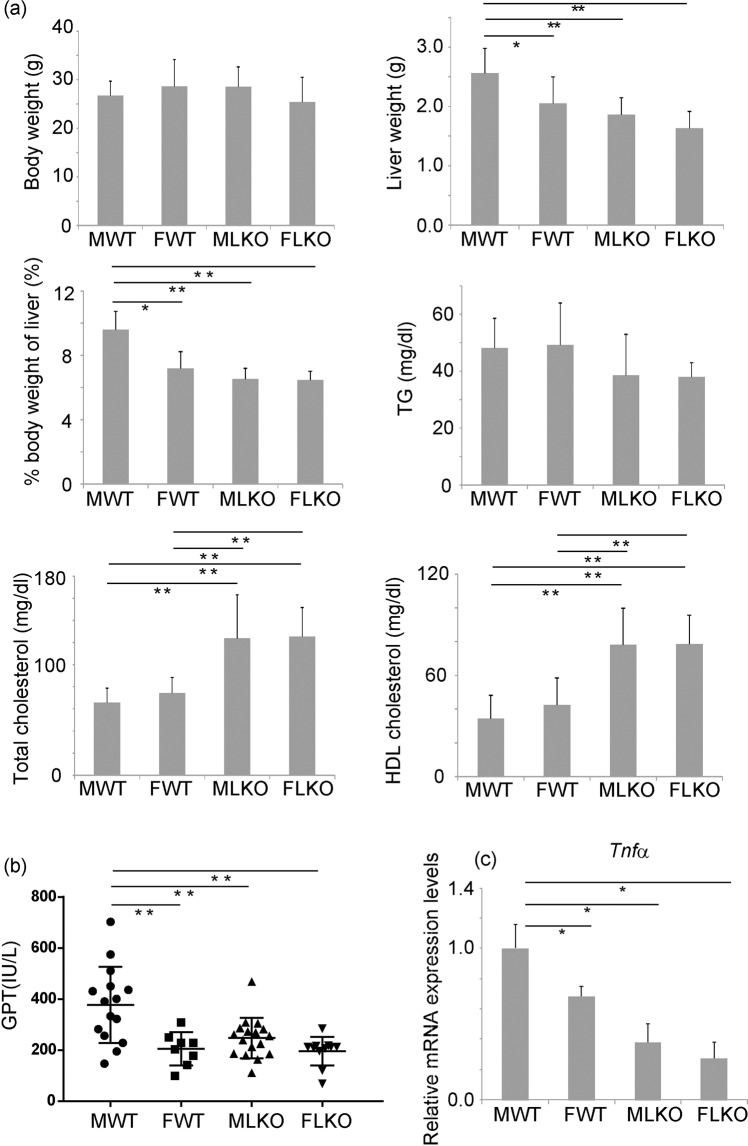
Figure 6.
Analysis of characteristics of Bcl6-LKO mice fed with CDAHFD for 38 weeks. (a) Body weight and liver weight were measured. The percent weight of liver relative to the body (% body weight of liver) weight was calculated. The serum levels of triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels were measured. Results are represented as mean ± standard deviation (S.D.) (n = 15 for male wild-type mice, n = 8 for female wild-type mice, n = 17 for male Bcl6-LKO mice, n = 11 for female Bcl6-LKO mice). (b) The serum levels of glutamic pyruvic transaminase (GPT) were measured as an indicator of liver injury. Results are represented as mean ± S.D. (n = 15 for male wild-type mice, n = 8 for female wild-type mice, n = 17 for male Bcl6-LKO mice, n = 11 for female Bcl6-LKO mice). (c) The mRNA expression levels of Tnfα mRNA in the liver were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. The Hprt gene was used as an internal control. The expression of genes in male wild-type mouse livers was set to 1.0. (n = 10 for male wild-type mice, n = 6 for female wild-type mice, n = 10 for male Bcl6-LKO mice, n = 10 for female Bcl6-LKO mice). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. MWT, male wild-type mouse samples; FWT, female wild-type mouse samples; MLKO, male Bcl6-LKO mouse samples; FLKO, female Bcl6-LKO mouse samples.