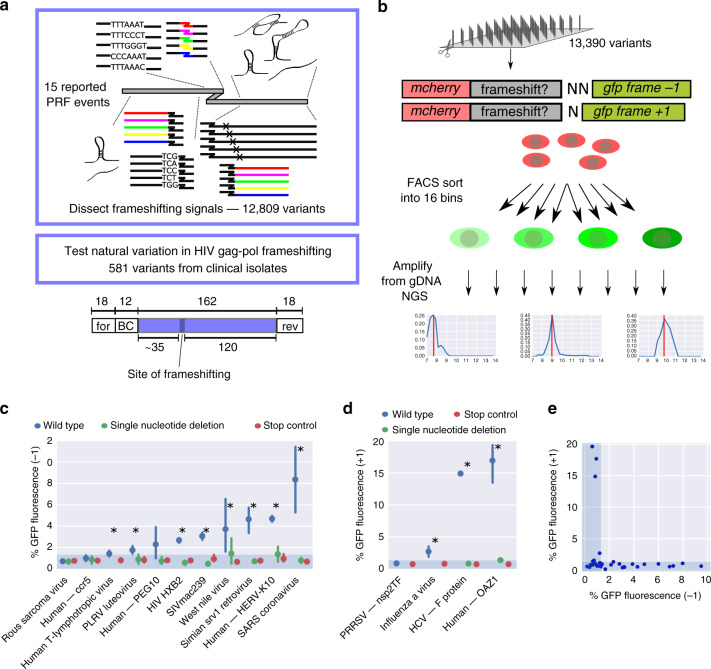
Fig. 1. A massively parallel reporter assay for programmed ribosomal frameshifting.
a Schematics of the library design; for forward primer, rev reverse primer, BC barcode. b Outline of the experimental pipeline; the plots in the bottom constitute representative bin profiles for variants with no (left), low (middle), or intermediate (right) GFP fluorescence. c, d Mean ± 95% CI of −1 (c) and +1 (d) PRF signal (% GFP fluorescence) for barcode control groups corresponding to the indicated wild-type PRF sequences (blue), carrying single nucleotide deletions (green) or having a stop codon inserted upstream of the frameshift sequence (red); n = 22, 2, 13, 32, 10, 25, 21, 8, 13, 24, 9 (c) and 2, 2, 1, 10 (d) wild-type sequences (blue), and n = 32, 7, 12, 33, 28, 23, 23, 21, 14, 23, 40 (c) and 11, 7, 19, 20 (d) sequences with deletion or stop codon (green and red) tested, in the order they appear on the graph; the shaded area denotes the range of background fluorescence; asterisks denote significant differences between the wild type and the other groups (single nucleotide deletion and stop control) combined (Mann–Whitney U test). e Comparison of −1 and +1 PRF reporter readout (% GFP fluorescence) for previously reported PRF sites (cf. c, d, Supplementary Fig. 3a, c).