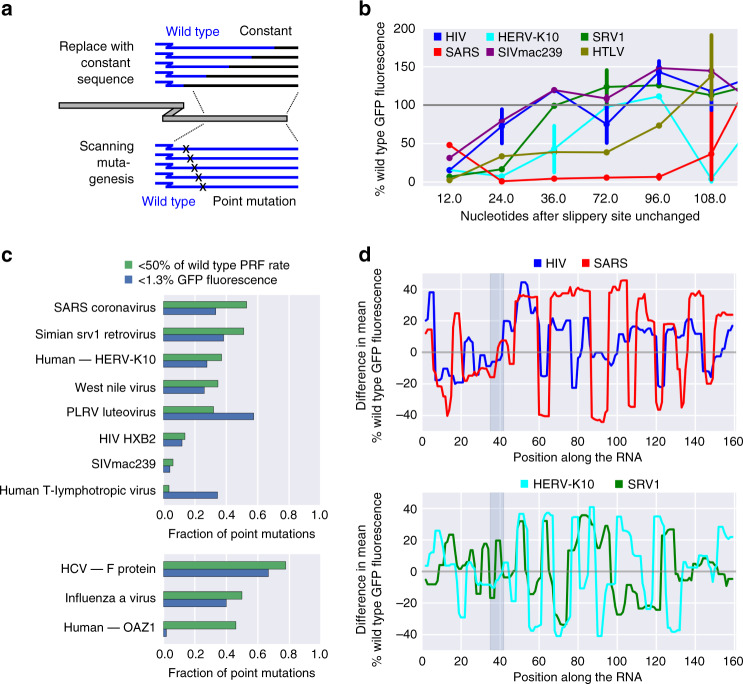
Fig. 3. PRF sites exhibit different sensitivities to changes in the downstream sequence.
a Schematic of downstream sequence manipulations. b Percent wild-type frameshifting rates of variants, in which the native downstream region has been replaced by constant sequences, leaving the indicated number of nucleotides after the slippery site unchanged; n = 1–3 per data point and PRF event. c Fraction of point mutations in the 40 nt downstream of the slippery site resulting in <50% of wild-type GFP fluorescence (green) and background fluorescence (<1.3% GFP fluorescence, blue), for −1 (top) and +1 (bottom) PRF events; n = 51, 47, 54, 23, 47, 51, 49, 29 (upper) and 9, 10, 52 (lower) sequences tested in total. d The difference in mean % wild-type frameshifting between variants, in which the indicated position is predicted to be paired vs. unpaired along the variable region; gray box: slippery site.