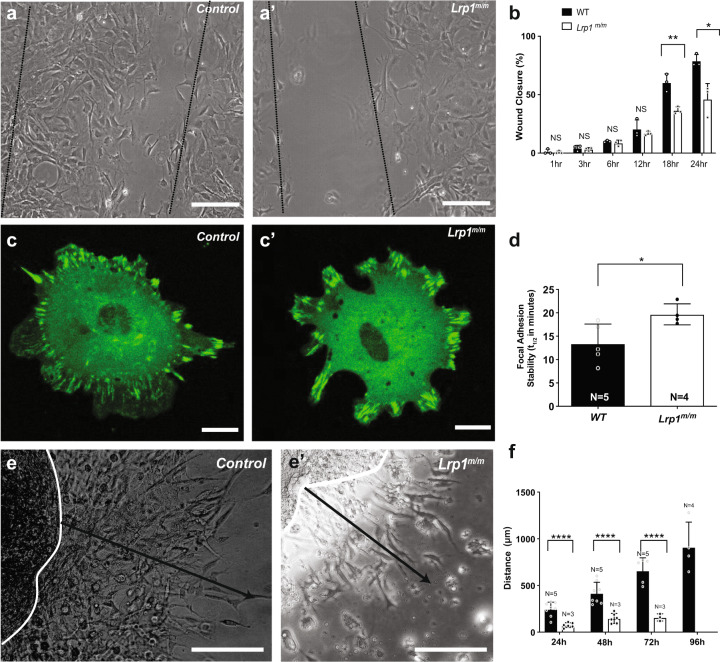
Fig. 7. Lrp1 mutation causes migration defects.
a, a′ Representative image of wound scratch assay from (a) a wild-type control and (a′) a mutant MEF, 18 h after scratch. b Quantitation of wound gap closure showed Lrp1m/m mutant MEFs have decreased cell motility compared to control with decreased filling of the scratch “gap” compared with controls. % indicates the percentage of closing the gap, 100% means close the gap completely. c Wild-type and (c′) Lrp1m/m mutant fibroblast cells were transfected with vinculin-GFP and vinculin turnover was measured using live-cell imaging. d Quantitative measurement revealed slower focal adhesion turn over in MEF from Lrp1m/m mutant, as measured by the half-life of the overlap between segmented focal adhesions at time 0 and time n. e, e′ Representative imagine of AVC explant migration assay from a wild-type control (e) and Lrp1m/m mutant (e′). Black line indicated the migration distance at 48 h. f Quantitative analysis of the distance of migration of endocardial cushion explants from E10.5 control and Lrp1m/m embryos showed near complete loss of cell migration from the Lrp1m/m mutant explants Statistical comparison was performed using unpaired two-way Student′s t test. Error bars show standard deviation.