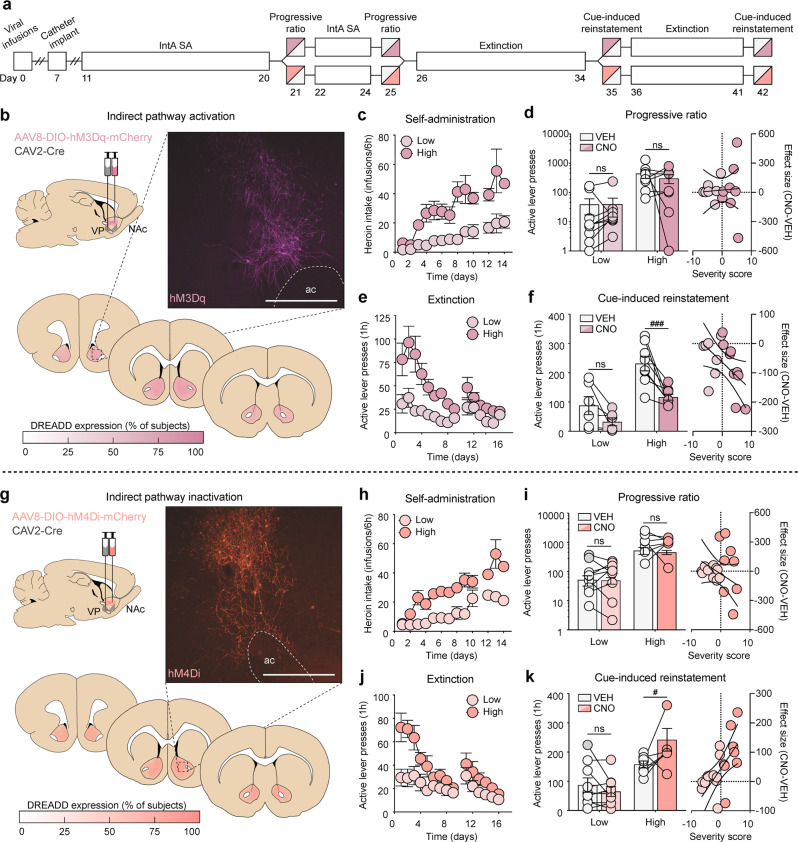
Fig. 5.
Transient modulation of iMSNs bidirectionally alters reinstatement but not motivation in high-risk rats. a Timeline for chemogenetic modulation of motivation under a PR schedule of reinforcement and cue-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking. b Viral strategy, representative histology, and quantification of expression for iMSN activation (low: n = 6; high: n = 8). c–f Self-administration, progressive ratio, extinction, and reinstatement data for iMSN-hM3Dq rats. d iMSN activation has no effect on motivation. Left: High-risk rats have greater responding for heroin than low-risk rats, which is unaffected by iMSN activation; right: CNO has no effect on motivation, regardless of addiction severity. f iMSN activation selectively reduces reinstatement in high-risk rats. Left: High-risk rats have greater responding for heroin cues than low-risk rats, which is selectively attenuated by CNO; right: the effect size of iMSN-hM3Dq significantly correlates with addiction severity. g Viral strategy, representative histology, and quantification of expression for iMSN inactivation (low: n = 9; high: n = 8). h–k Self-administration, progressive ratio, extinction, and reinstatement data for iMSN-hM4Di rats. i iMSN inactivation has no effect on motivation. Left: High-risk rats have greater responding for heroin than low-risk rats, which is unaffected by iMSN inactivation; right: CNO has no effect on motivation, regardless of addiction severity. k iMSN inactivation selectively enhances reinstatement in high-risk rats. Left: High-risk rats have greater responding for heroin cues than low-risk rats, which is selectively enhanced by CNO; right: the effect size of iMSN-hM4Di significantly correlates with addiction severity. Scale bar = 500 μm; ac, anterior commissure; #p < 0.05 (VEH vs CNO), ###p < 0.001 (VEH vs CNO).