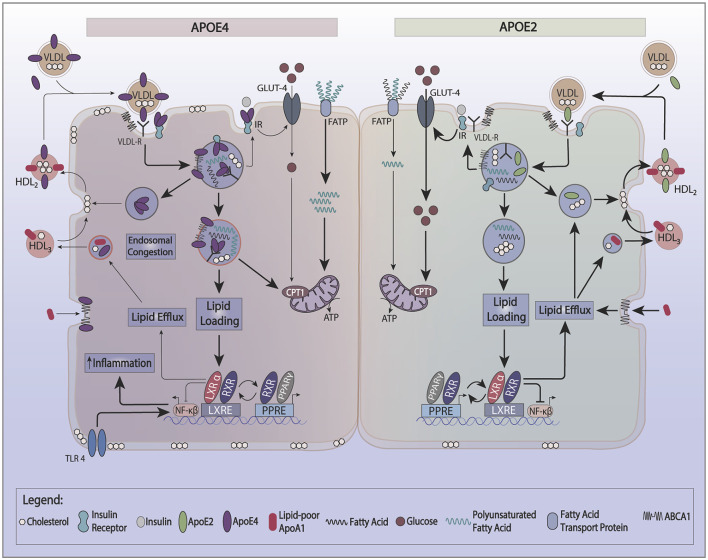
Figure 1.
Effect of apoE recycling and aggregation on glucose and lipid metabolism. ApoE recycling controls the expression of several cell surface proteins, such as the insulin receptor (IR), ATP bindingcassette 1 (ABCA1), or lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP-1). The formation of smaller HDL3 by ABCA1 stimulates apoE recycling. In the circulation, apoE exchanges between HDL and VLDL. Upon lipid loading, the expression of apoE, ABCA1, and ABCG1 is induced via the PPAR/LXR/RXR system to facilitate lipid storage or oxidation and formation of HDL. ApoE4 is prone to aggregate in endosomes trapping interacting proteins such as IR and ABCA1. ApoE4’s switches the cellular energy preference from glucose to polyunsaturated fatty acids, and associates with lower ABCA1 activity and greater cell membrane cholesterol. Greater cell membrane cholesterol enhances TLR4 signaling and activates the inflammasome. ApoE4 also decreases the activation of PPARγ contributing to lower insulin sensitivity and utilization of glucose as a source of ATP.