Figure 2.
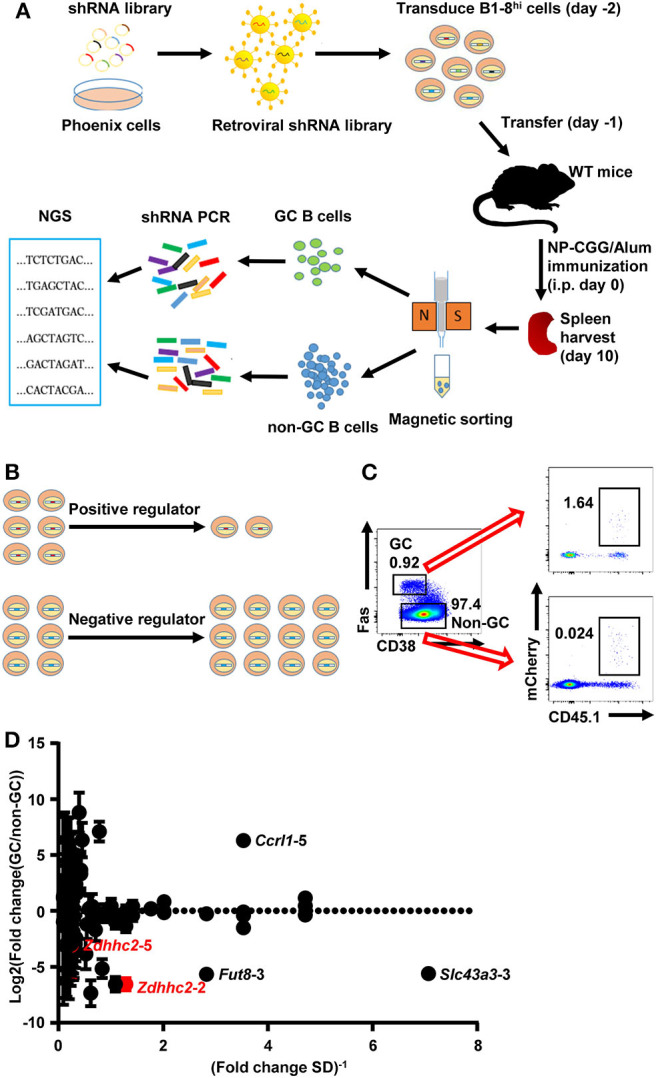
Overview of the shRNA in vivo screening system for regulators of germinal center (GC) B cell differentiation. (A) A schematic view of the in vivo screening system for regulators of GC B cell differentiation. The shRNA retroviral library was produced in Phoenix cells and used to transduce B1-8hi cells on day−2, which were adoptively transferred into eight wild-type (WT) recipient mice on day−1. These mice were immunized with NP-CGG/Alum on day 0, sacrificed on day 10, and subjected to splenic GC and non-GC B cell isolation by magnetic sorting. The shRNA sequences were amplified by PCR and determined by next-generation sequencing to evaluate the abundance of each shRNA construct. (B) Illustration of the screening strategy: shRNA constructs that target the positive regulators of GC B cell differentiation are less abundant and vice versa for negative regulators. (C) Representative flow cytometry profiles showing the percentages of retroviral shRNA library transduced cells (expressing mCherry) in GC and non-GC B cells in mice treated as described in (A). (D) Plot of the binary logarithm of shRNA's fold change values (calculated as the ratio of each shRNA's abundance in GC B cells to that in the corresponding non-GC B cells) against the reciprocals of their standard deviations [(fold change SD)−1]. Two independent screens were performed.
