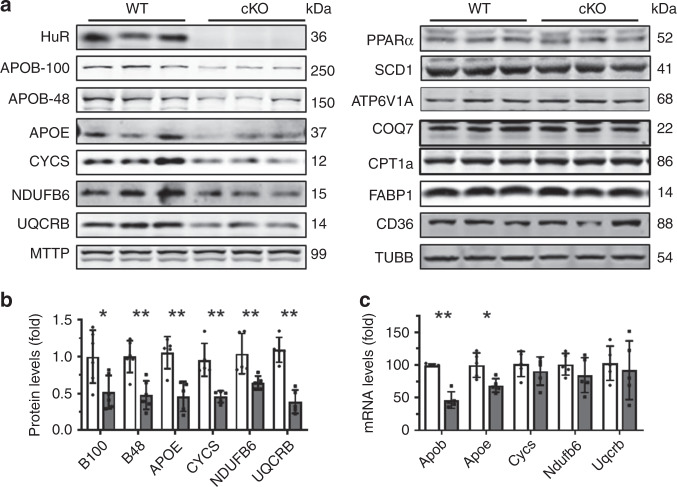
Fig. 2. Liver HuR ablation reduces the levels of factors that regulate lipid transport and ATP synthesis.
a Protein lysates prepared from liver tissues described in Fig. 1a were subjected to Western blot analysis to assess the levels of proteins HuR, APOB-100, APOB-48, APOE, CYCS, NDUFB6, UQCRB, MTTP, PPARa, ATP6V1A, SCD1, ATP6V1A, COQ7, CPT1a, FABP1,CD36, and β-Tubulin (TUBB). Blots were processed from parallel gels. b The density of the signals for APOB-100 (B100), APOB-48 (B48), APOE, CYCS, NUUFB6, and UQCRB [APOB-100 and APOB-48, WT and cKO, n = 6; others, WT and cKO, n = 5)] in a was calculated and plotted as the means ± SD; significance was assessed by using two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). Blank columns, WT; Black columns, cKO. c RNA prepared from tissues described in a was subjected to RT-qPCR analysis to assess the levels of Apob, Apoe, Cycs, Ndufb6, and Uqcrb mRNAs (WT and cKO, n = 5). Data are the means ± SD (Blank columns, WT; Black columns, cKO); significance was assessed by using two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). All the error bars are equivalent throughout the figure. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.