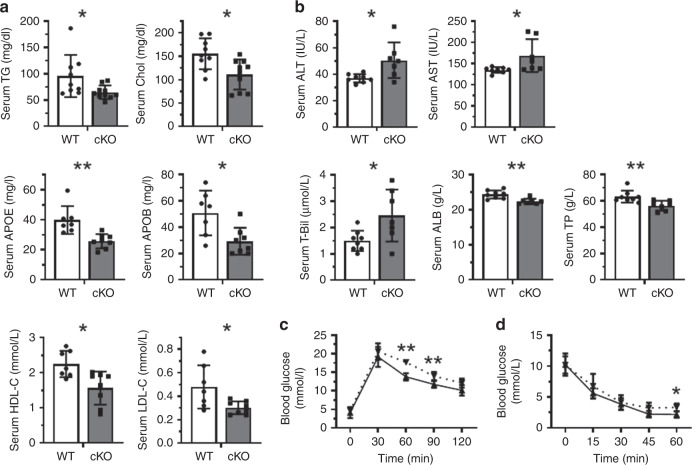
Fig. 4. Liver HuR deficiency impairs liver function in HFD mice.
a HuR cKO mice and WT littermates were fed with HFD for 4 weeks, whereupon the levels of triglyceride (TG), cholesterol (Chol), APOB, APOE, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in the serum were analyzed (TG and Chol, WT, n = 9, cKO, n = 10; others, WT, n = 7, cKO n = 8). b The serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin (T-Bil), albumin (ALB), and total protein (TP) were analyzed (WT, n = 8; cKO, n = 7). c Mice described in a were starved overnight (WT, n = 6; cKO, n = 6) and injected intraperitoneally with glucose (1 g/kg), and serum collected from tail vein at the times indicated were used to analyze the levels of glucose (glucose tolerance test, GTT) by using a glucometer (BAYER). Dotted line, HuR cKO; solid line, WT. d Mice described in a (WT, n = 5; cKO, n = 7) were starved for 6 h and injected intraperitoneally with insulin (0.85U/kg). The levels of glucose in the serum (insulin tolerance test, ITT) were analyzed as described in c. Dotted line, HuR cKO; solid line, WT. Data in a–d are the means ± SD; significance was analyzed by two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). All the error bars are equivalent throughout the figure. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.