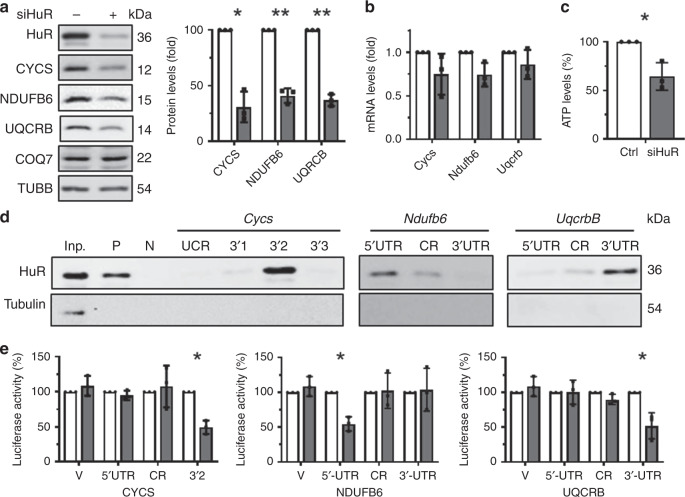
Fig. 7. HuR promotes ATP synthesis at least in part by regulating the levels of CYCS, NDUFB6, and UQCRB.
a, b Mouse Hepa1–6 cells were transfected with HuR-directed or control siRNAs; 48 h later, protein lysates and RNA prepared from cells were subjected to western blot analysis (a) and RT-qPCR analysis (b), respectively, to assess the levels of HuR, CYCS, NDUFB6, COQ7, UQCRB, and TUBB proteins (a) as well as the levels of Cycs, Ndufb6, and Uqcrb mRNAs (b), respectively. Blank columns, control; Black columns, siHuR. c Cells described in a were subjected to ATP analysis. d RNA pull-down assays were performed by using Hepa1–6 cell lysates and in-vitro-transcribed RNAs depicted in Supplementary Fig. 16a. p27 5′UTR and CR (coding region) served as positive (P) and negative (N) controls, respectively. A 5-µg aliquot input (Inp.) and binding to TUBB were also assessed. Data are representative from three independent experiments. e Hepa1–6 cells were transfected individually with each of the reporters depicted in Supplementary Fig. 16d. Twenty four hour later, cells were further transfected with a HuR siRNA or a control siRNA and cultured for an additional 48 h, whereupon the relative luciferase activities were determined. Blank columns, control; Black columns, siHuR. Data in panels (a–c and e) are the means ± SD from three independent experiments; significance is analyzed by two-tailed Student’s t-test (**p < 0.01). All the error bars are equivalent throughout the figure. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.