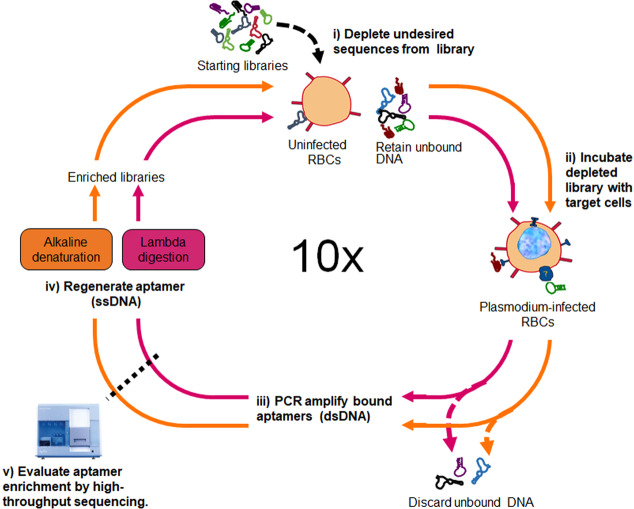
Figure 1.
A parallel SELEX scheme was employed to select aptamers to P. falciparum-infected red blood cells (RBCs). (i) Combinatorial ssDNA libraries, consisting of oligonucleotides with a centrally randomized region of 45 nucleotides flanked by specific primers, are removed of sequences that bind to uninfected RBCs in a negative selection step. (ii) The depleted libraries are incubated with P. falciparum-infected RBCs to enforce selection of aptamers binding determinants unique to infected erythrocytes (IEs). (iii) Following thorough washing, bound sequences are amplified by PCR. (iv) Aptamers are regenerated as ssDNA either by alkaline denaturation or digestion with lambda exonuclease. The resulting enriched ssDNA pools are used in the next round of the negative selection, positive selection, and amplification. In the 10th SELEX round, the selected ssDNA from the two independent selections are analyzed for aptamer enrichment using the Illumina high throughput sequence platform.