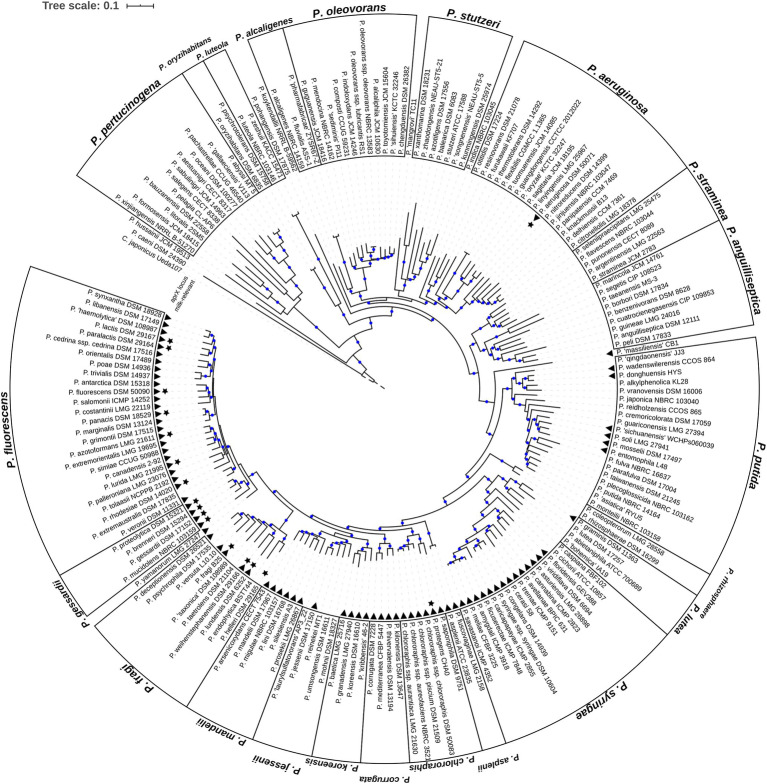
Figure 1.
Phylogenomic tree of the genus Pseudomonas. Shown is the rooted maximum likelihood phylogenomy of the genus Pseudomonas comprising 185 type strains. The tree is based on a multiple sequence alignment composed of 92 universal bacterial core genes (69,704 alignment positions). Evolutionary distances were estimated using the GTR+G+I model. Branches with high bootstrap support (≥70%) are marked with blue circles. In total, 200 bootstrap replicates were calculated. Cellvibrio japonicus Ueda107T (RefSeq ID NC_010995.1) is used as outgroup. For reasons of clarity the length of the outgroup branch was downscaled to 0.05 substitutions per site (dashed branch). Black triangles highlight type strains containing the aprX gene. Black stars refer to type strains of species classified as milk-relevant in the past. The genus is separated into 22 distinct monophyletic groups and 8 singletons. Group names are shown at the outer-most border.