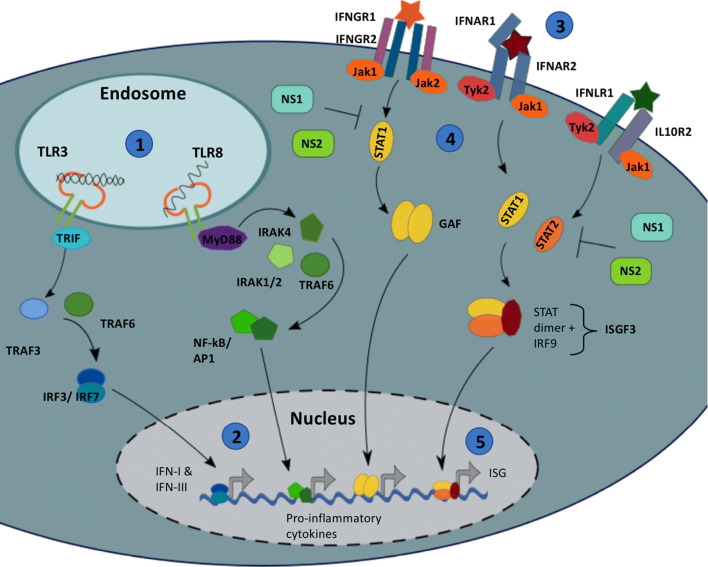
Fig. 3.
TLR & IFN signalling. (1) Toll-like Receptor 3 & 8 detect intracellular pathogens by detecting dsRNA and ssRNA, respectively. Once initiated, signalling cascades activate transcription factors, (2) which upregulate anti-viral IFNs (Type I, II and III) and pro-inflammatory cytokines. (3) IFNs act on the infected and neighbouring cells by binding the Interferon receptors (e.g. IFNAR). (4) Change in receptor conformation allows the receptor-associated kinases, Tyk and Jak1, to trans-phosphorylate, which in turn phosphorylate receptor subunits, providing docking sites for STAT proteins. (5) Receptor-associated STATs become phosphorylated, dissociate from the receptor and form homo- or hetero-dimers. The IFN-α-activated STAT1:STAT2 dimer binds IRF9, forming a complex that translocates to the nucleus and stimulates the expression of Interferon Sensitive Genes (ISGs). RSV NS proteins have been shown to inhibit IFN signal transduction by impairing STAT activation