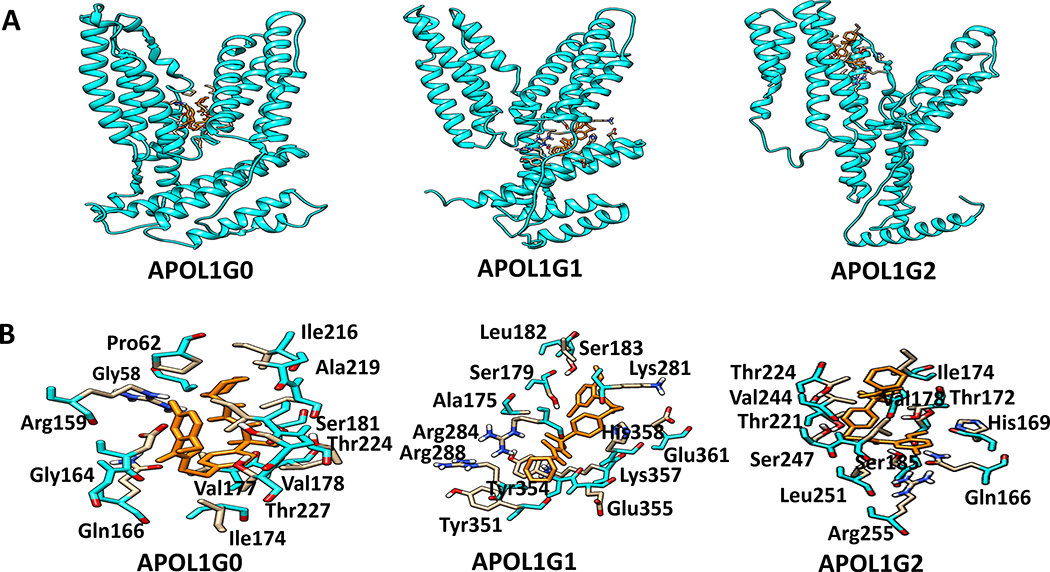
Figure 11. The docking of a specific ATP sensitive K+ Efflux inhibitor on APOL1.
A. Binding sites of K+-efflux on APOL1 and its variants are displayed. Binding site of Glyburide (orange) in the APOL1G0, APOL1G1 and APOL1G2 structures.
B. Glyburide (orange) interacting residues. The Glyburide interacting residues in ApoL1G0 include Arg159, Pro62, Leu220, Ile216, Ser181, Val177, Gln166, Asp163, Ala57, Ile223, Thr224, Thr227, and Val178. The residue Arg284 forms a hydrogen bond with Glyburide. In the ApoL1G1-Glyburide complex, the glyburide interacting residues include Ser179, Leu182, Ser183, Lys281, Glu361, His358, Tyr354, Glu355, Arg288, Arg284, Lys357, and Tyr351. The residue Arg284 forms a hydrogen bond with Glyburide. The Glyburide interacting residues in ApoL1G2 include Thr224, Val244, Ser247, Leu251, Arg255, Gln166, His169, Ser185, Ser181, Thr221, Val178, and Leu248. The residue Ser185 forms hydrogen bond with Glyburide.