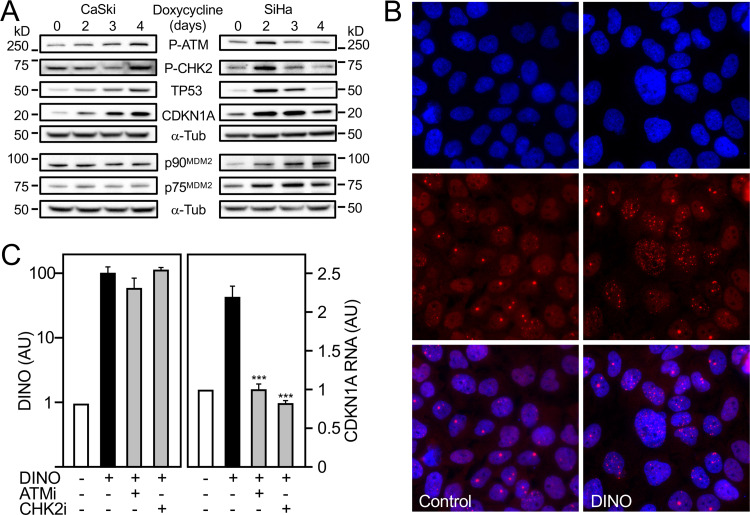
FIG 8.
Acute DINO expression induces hallmarks of DNA damage signaling. HPV16-positive CaSki (left) and SiHa (right) cervical cancer lines with inducible DINO expression were treated with 1 μg/ml doxycycline, and levels of phospho-Ser1981 ATM (P-ATM), phospho-Thr68 CHK2 (P-CHK2), TP53, CDKN1A, and the p90 and p75 MDM2 isoforms were assessed by immunoblot analysis with α-tubulin (α-Tub) serving as a loading control. The MDM2 blotting assays were performed in a separate experiment but using aliquots of the same protein extracts as those used for the other blotting assays. The positions of marker proteins with their apparent molecular weights in kilodaltons (kD) are indicated (A). Nuclear 53BP1 foci in CaSki cells in control and after doxycycline-mediated DINO expression. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Representative immunofluorescence microscopy images are shown; similar results were obtained in two independently performed microscopy experiments. Top panels show DAPI-stained nuclei, middle panels show nuclear 53BP1 foci, and lower panels show merged images (B). CaSki cells with inducible DINO expression were treated with 1 μg/ml doxycycline and 10 μM ATM inhibitor KU-55933 (ATMi) or 5 μM CHK2 inhibitor BML-277 (CHK2i), and expression of DINO and the canonical transcriptional TP53 target gene CDKN1A was determined by qRT-PCR. Expression data are presented in arbitrary units (AU) and are normalized to expression of the RPLP0 housekeeping gene. Bar graphs represent means ± SEM (n = 3). ***, P < 0.001 (Student’s t test) (C).