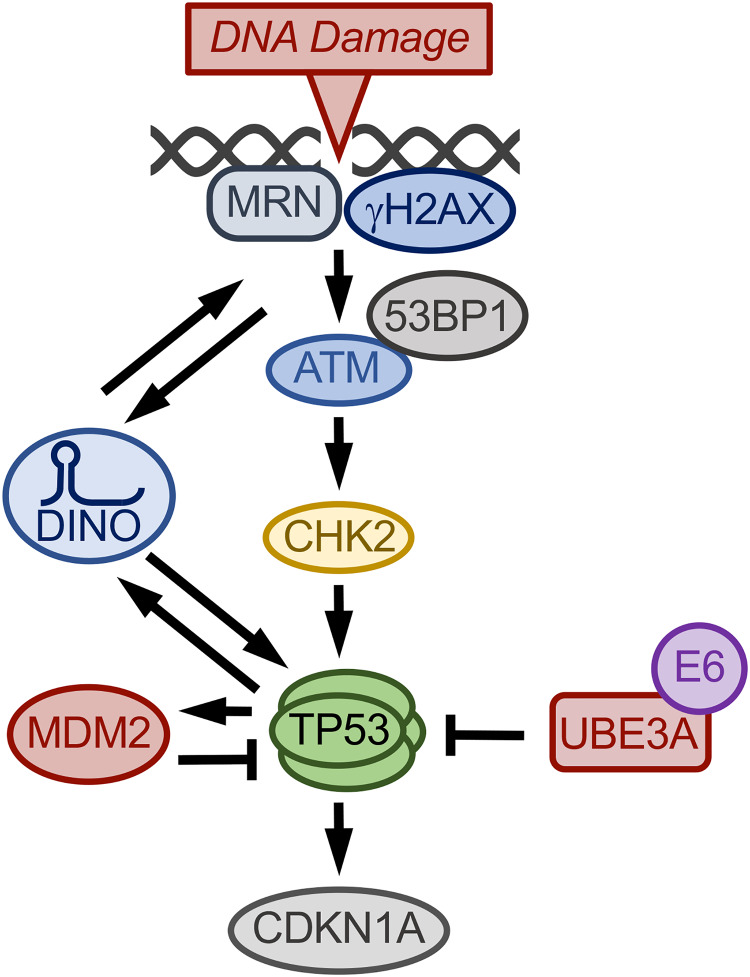
FIG 9.
Model of DINO regulation in HPV-positive cervical cancer cells. In response to DNA damage, DINO is induced through an ATM/CHK2/TP53-independent mechanism. DNA damage also triggers TP53 activation through ATM/CHK2-dependent signaling, which causes increased expression of TP53 transcriptional target genes, including CDKN1A and DINO. DINO further activates TP53 by inducing hallmarks of the DNA damage response signaling pathway as evidenced by 53BP1 nuclear foci and ATM and CHK2 activation. By binding to DNA-bound TP53 transcription factor complexes, DINO may enhance TP53 transcriptional activity. DINO activity is balanced by TP53-mediated MDM2 upregulation as well as the E6/UBE3A complex, which targets TP53 for proteasomal degradation.