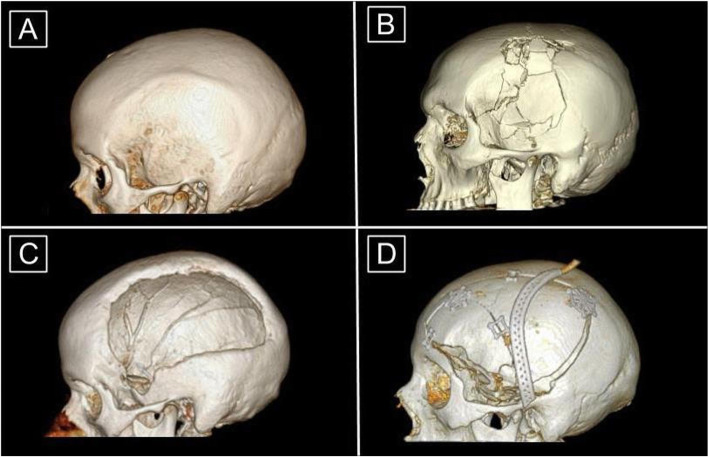
Fig. 1.
3D Reconstructions of Head CT Images in Craniectomy and Cranioplasty (a) Intact or normal skull. (b) Skull fracture that is overlying intracranial pathology requiring craniectomy. (c) Cranial defect after craniectomy. Note the asymmetric and heterogeneous nature of the outer border. (d) Post-operative subject who had undergone cranioplasty with autologous bone. The perforated piece overlying the skull is a Jackson-Pratt drain. Note that the bone fragments require extra structural support and do not fully repair the cranial defect along the inferior border