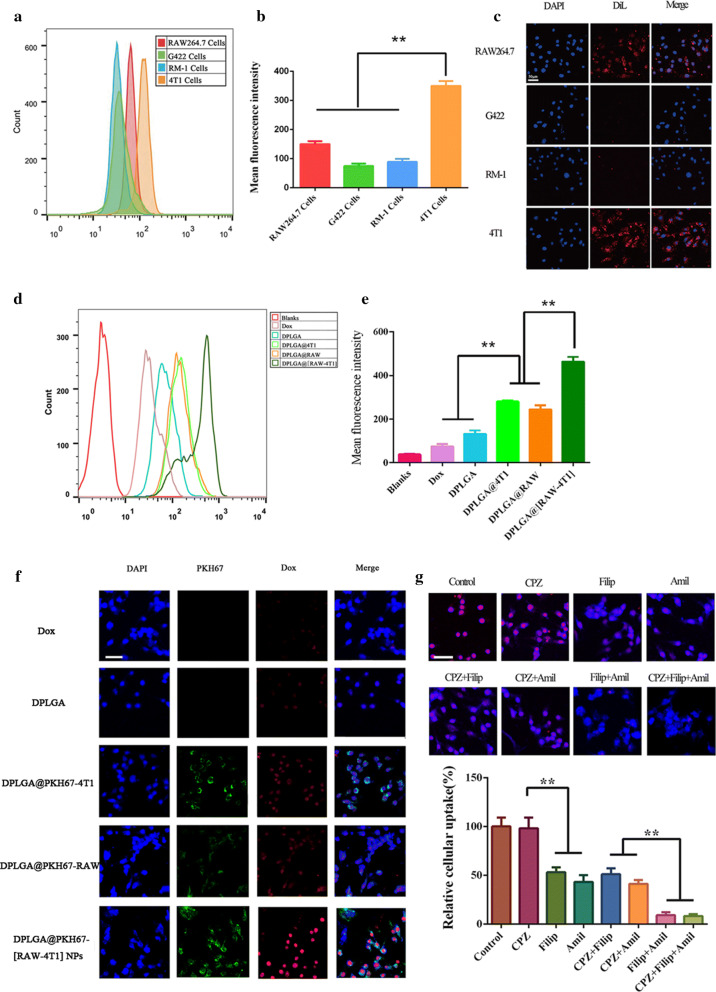
Fig. 2.
In vitro targeting and transmembrane mechanism of DPLGA@[RAW-4T1] NPs. a Flow cytometry detection results and b mean fluorescence intensity obtained in four different cell types (RAW264.7, G422, RM-1, 4T1) upon 4 h treatment with DiL-labeled PLGA@[RAW-4T1] NPs. c Confocal microscopic images of RAW264.7 cells, G422 cells, RM-1 cells, and 4T1 cells cultured with DiL dyed PLGA@[RAW-4T1] NPs. Scale bar = 50 μm. d Mean fluorescence intensity analysis in flow cytometry detection of 4T1 cells incubated with blank solution, free Dox, DPLGA NPs, DPLGA@4T1 NPs, DPLGA@RAW NPs, and DPLGA@[RAW-4T1] NPs. e Confocal microscopic observation in 4T1 cells after treatment with blank solution, Dox, DPLGA NPs, DPLGA@4T1 NPs, DPLGA@RAW NPs, or DPLGA@[RAW-4T1] NPs. f Cellular internalization of DPLGA@[RAW-4T1] NPs was scanned using a confocal microscope. Scale bar = 50 μm. g Impact of inhibitors of endocytic pathways on cell uptake of DPLGA@[RAW-4T1] NPs on 4T1 cells. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05 was regarded to indicate a significant difference between these two groups