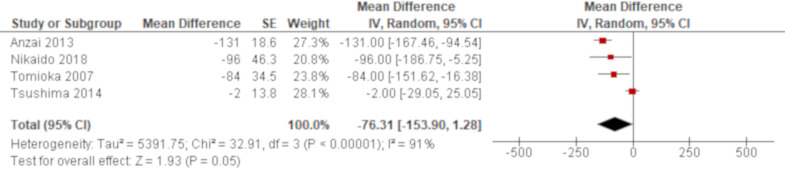
Figure 4.
Forest plot of the result of univariate analysis for partial pressure of arterial oxygen/ fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2) ratio (combined by mean difference (MD)). The result of univariate analysis in four studies was pooled for meta-analysis and a total of 118 patients were included. There was no significant difference of PaO2/FiO2 ratio between non-survivors and survivors with a MD of −76.3 mmHg (95% CI −153.9 to 1.28, p=0.05). There was substantial heterogeneity with statistical significance (χ2=32.91, p<0.00001, I2=91%). The 95% prediction interval ranged from −435.2 to 282.6. All studies were conducted in Japan and implemented nearly the same definition of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The number of included patients was 50 or fewer in all studies. The effect of one study67 was extremely different from that of the other three studies. It analysed 28-day all-cause mortality whereas the other three studies analysed either in hospital, 60 days or overall all-cause mortality.