FIGURE 4.
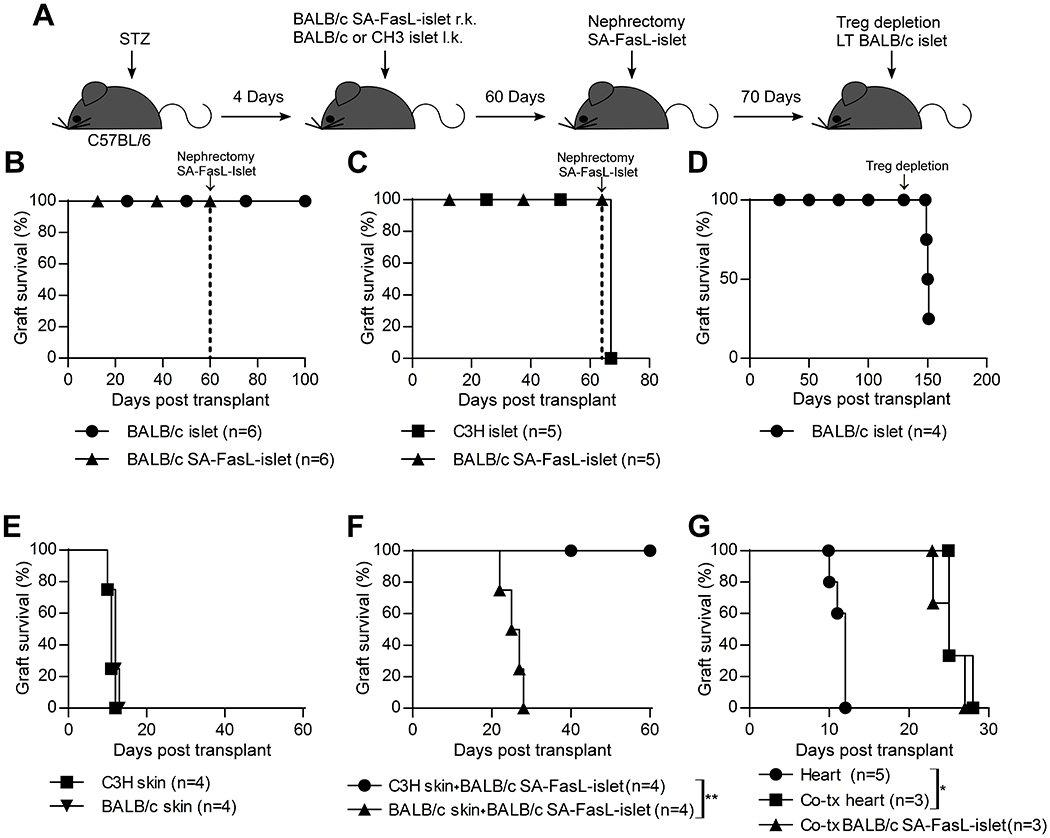
Tolerance to SA-FasL-engineered islet grafts is donor-specific and systemic at the induction phase. A, Schematic diagram showing the study design. Chemically diabetic C57BL/6 mice were transplanted with SA-FasL-engineered BALB/c islets under the right kidney capsule and unmodified BALB/c (B) or C3H (C) islet grafts under the contralateral kidney capsule. Mice were subjected to a short course of rapamycin treatment (0.2 mg/kg daily for 15 doses starting the day of transplantation). B, Surgical removal of the kidney harboring SA-FasL-engineered BALB/c islet graft 60 days post-transplantation (arrow) did not result in hyperglycemia, demonstrating the survival and function of unmodified donor-matched islets. C, Surgical removal of SA-FasL-engineered BALB/c islet graft (arrow) results in prompt hyperglycemia in the cohort harboring unmodified C3H third party islet graft under the contralateral kidney capsule, demonstrating rejection. D, Ablation of Treg cells in mice shown in panel B (after surgical removal of the kidney harboring the SA-FasL-engineered islets) using an antibody to CD25 (PC.61) on day 130 post-transplantation (arrow) resulted in rejection of 3 out of 4 grafts, demonstrating the role of Treg cells in maintaining survival of the unmodified islet graft. E, Survival of BALB/c donor and C3H third party skin grafts in C57BL/6 recipients simultaneously transplanted with BALB/c SA-FasL-engineered islet grafts. F, Rejection of BALB/c, but not third party C3H, skin results in prompt rejection of SA-FasL-engineered islets (MST = 26 ± 2.6 days, log-rank comparison of islet survival p = 0.0067). G, SA-FasL-engineered islets do not induce tolerance when co-transplanted with donor-matched heart grafts. Chemically diabetic C57BL/6 were transplanted with SA-FasL-engineered islets under the kidney capsule and donor-matched heart graft in the abdomen. A separate group was transplanted with heart only under a brief course of rapamycin to serve as control. Both graft types are rejected with heart graft showing prolonged survival as compared with the control (MST 25 ± 1.7 vs 12 ± 0.9 days, log-rank comparison of heart survival p = 0.0074).
