Figure 5.
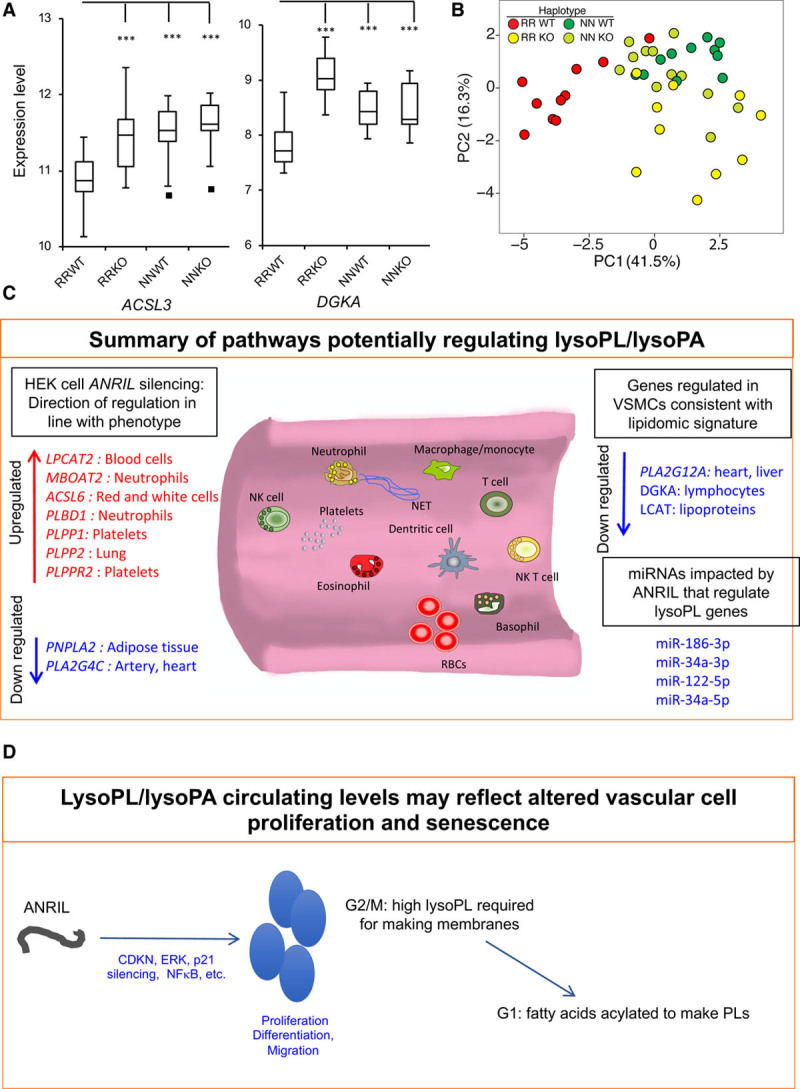
VSMCs from risk haplotypes show differential gene expression of lysoPL (lysophosphospholipid) metabolizing genes that are rescued by deletion of the Chr9p21 locus.
A, PCA shows that the presence of risk haplotypes is associated with differential gene expression of lysoPL genes. Induced pluripotent stem cells from peripheral monocytes were obtained and differentiated as described in Materials in the Data Supplement. RNAseq data were clustered using lysoPL metabolizing genes by PCA in R. Nonrisk haplotype (NNWT), risk haplotype (RRWT) and their genome edited counterparts (NNKO and RRKO) are shown. B, Example data sets for ACSL3 and DGKA, showing that removing the risk locus reverts gene expression back to levels in nonrisk individuals. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005, Students t test, n=9–10 clones per group. C and D, Schematics showing impact of ANRIL silencing or risk haplotypes on relevant lysoPL metabolizing genes. PCA indicates principal component analysis; PC1, principal component-1; and VSMCs, vascular smooth muscle cells.
