Fig. 4.
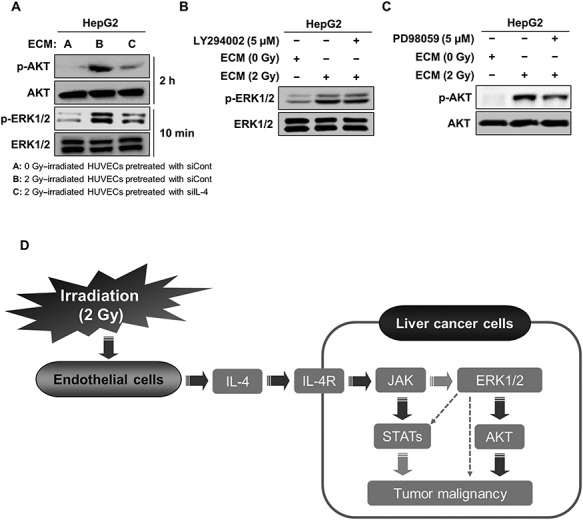
The activation of the IL-4/ERK/AKT pathway contributed to the increase in the malignancy of HepG2 cells treated with 2 Gy–irradiated ECM. (a) Western blot analysis of the levels of phosphorylated AKT and ERK after treatment of HepG2 cells with conditioned medium from 2 Gy–irradiated HUVECs pretreated with siRNA targeting IL-4 for 2 h and 10 min, respectively. (b) Effects of LY294002 on the protein level of phosphorylated ERK in HepG2 cells treated with 2 Gy–irradiated ECM. Cells were grown in the presence or absence of LY294002 (5 μM) for 10 min, and western blot analysis was performed. (c) Effects of PD98059 on the protein level of phosphorylated AKT in HepG2 cells treated with 2 Gy–irradiated ECM. Cells were grown in the presence or absence of PD98059 (5 μM) for 2 h, and western blot analysis was performed. (d) Proposed mechanism underlying the increase in the malignancy of liver cancer cells in response to 2 Gy–irradiated ECM. Western blotting was performed in triplicate, and the data shown are representative of a typical experiment.
