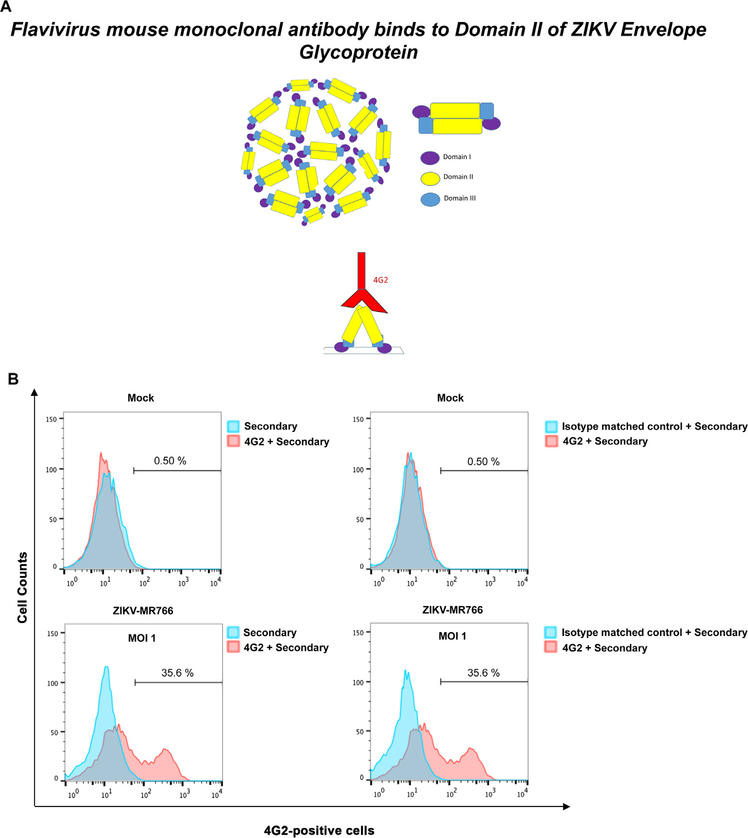
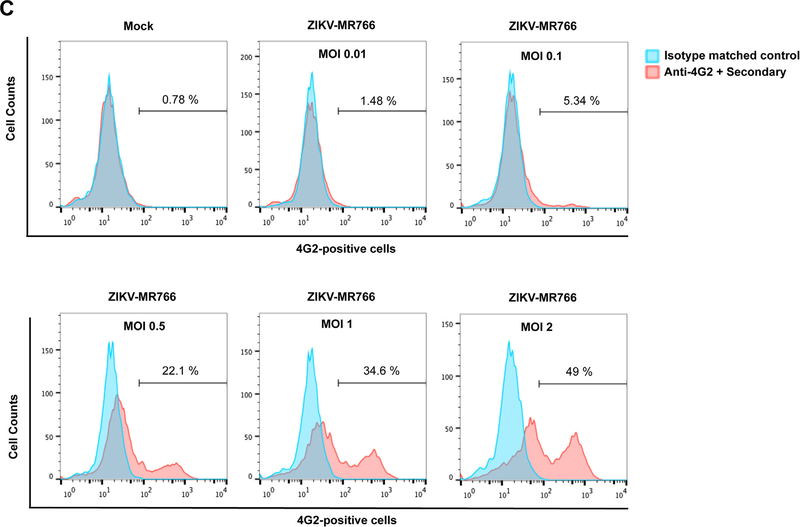
Fig. 2. Detection of wild type ZIKV infection using the anti-envelope monoclonal antibody 4G2.
(A) The domains I, II and III of the ZIKV envelope glycoprotein are depicted. The mouse monoclonal antibody 4G2 (red) binds to the fusion loop of Domain II. (B) The monoclonal antibody 4G2 recognizes ZIKV-infected Vero cells. Vero cells were challenged by ZIKV strain MR766 (ZIKV-MR766) at an MOI of 1 (lower panels). Twenty-four hours post-challenge cells were fixed/permeabilized, and infection was determined by staining cells using anti-ZIKA envelope antibodies 4G2. The percentage of infected cells was measured by counting the number of 4G2-positive cells using a flow cytometer. As a control, fixed/permeabilized infected cells were also stained using an isotype matched control antibody. We performed similar experiments using fixed/permeabilized mock infected cells. (C) Infection of Vero cells by ZIKA viruses at different MOIs. Vero cells were challenged by ZIKA-MR766 at increasing MOIs. The percentage of infected cells was measured by counting the number of 4G2-positive cells using a flow cytometer. Experiments were performed at least three times and a representative experiment is shown.