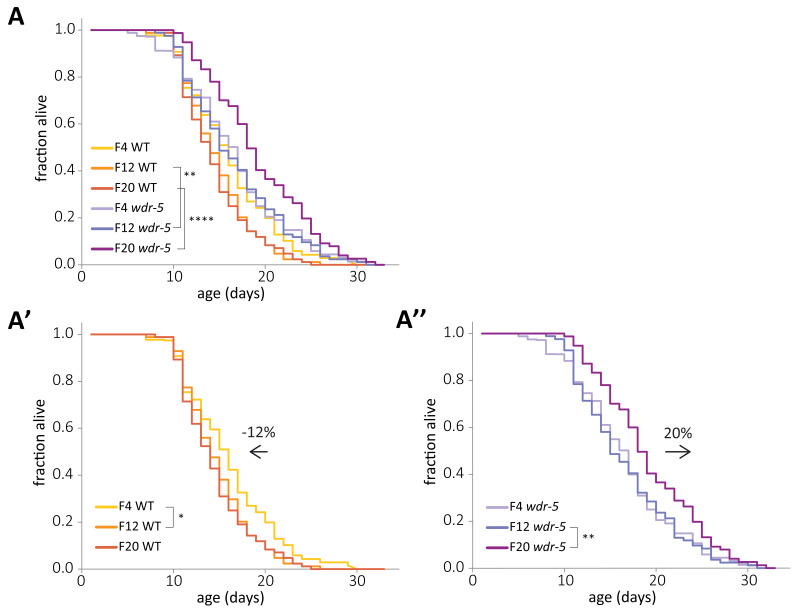
Figure 2. Concurrent and opposite changes in lifespan account for the full wdr-5 mutant lifespan extension.
(A) Lifespan of early-, mid-, and late-gen wild-type (yellow, tangerine, and burnt orange, respectively) and wdr-5 mutant populations (lavender, purple, and plum, respectively) descended from animals recovered from a thaw. Data are also shown separated into wild-type (A’) and wdr-5 mutant populations (A’’). Percentage difference in median lifespan between early- and late-gen is indicated above arrow. p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ****p<0.0001 using log-rank test. Median lifespan and statistics are presented in supplementary file 1. Additional replicates are included in supplementary file 3.