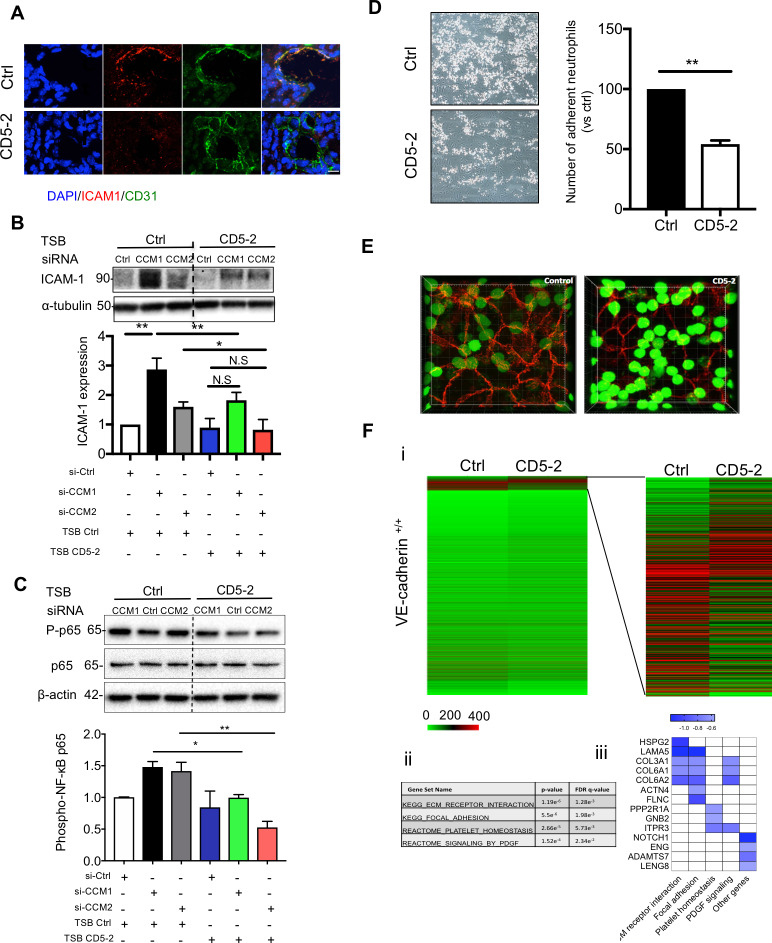
Fig 6. CD5-2 inhibits inflammatory response in CCM lesion via VE-cadherin.
(A) CD5-2 effects on ICAM-1 expression in CCM lesion. Sections were triple-stained for DAPI (blue) or CD31 (green), ICAM-1 (red); 3 mice were utilized for each condition. Representative sections are shown. Bar, 8 μm. (B-C) Western blot analysis of ICAM-1 (B) and phospho-p65 (C) in brain microvascular ECs (hCMEC/D3) treated with 10 nM siRNAs for scramble control (Ctrl), CCM1, or CCM2 for 4 hours, followed by transfection of 15 nM CD5-2 or controls then cultured overnight. Molecular weights in kilodaltons are shown. ICAM-1 antibody (Cell signalling #4915) gave two bands (89 and 92 kDa). This antibody recognizes the ICAM-1 C-terminal portion, which is dense with ubiquitination and phosphorylation sites and, as such, #4915 can detect multiple sized ICAM moieties. Representative blots are shown (n = 3) with α-tubulin or β-actin rabbit used as loading control. (D) Representative images of dynamic adhesion of neutrophils to control- or CD5-2–treated ECs following the stimulation with TNF-α for 4 hours. Quantification of number of adherent neutrophils with control or CD5-2–treated ECs is given (n = 3). (E) Representative images of paracellular transmigration of neutrophils (green) through TNF-α–stimulated endothelium (VE-cadherin, red) in the presence of control and CD5-2 in vitro. Transmigrated neutrophils appear GFPdim. (F) (i) Heatmap of all genes between control (Ctrl) and CD5-2 (CD5-2) in VE-cadherin–expressing ECs (VE-cadherin+/+). (ii) GSEA analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between Ctrl- and CD5-2–treated ECs. (iii) Bar plot of selected inflammation-related DEGs inhibited by CD5-2. Values are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, N.S, not significant, determined by Student t test or one-way ANOVA with Tukey correction. For the raw data used for quantification, see Fig 6 in S1 Data; Fig 6B and 6C in S1 Raw images. CCM, cerebral cavernous malformation; CD31, cluster of differentiation 31; EC, endothelial cell; GFP, green fluorescent protein; GSEA, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis; hCMEC/D3, human cerebral microvascular endothelial cell line; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; siRNA, small interfering RNA; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; TSB, target site blocker; VE-cadherin, vascular endothelial cadherin.