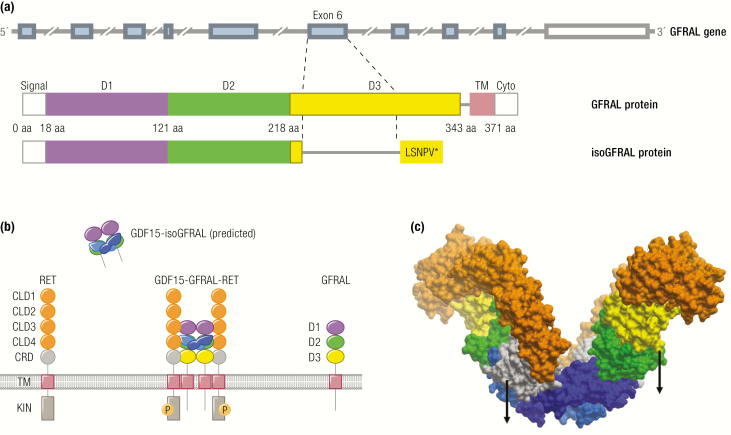
Figure 3.
The GDF15-GFRAL-RET complex. The same color scheme is used to highlight the protein domains in all 3 panels. A: The gene structure of the human GRFAL alongside a schematic domain arrangement of the full-length GFRAL protein and its splice variant isoGFRAL. The coding exons are highlighted in light blue, with the 3’ UTR shown in white. GFRAL domains are labelled signal (signal peptide), D1-3 (GFR-like domain 1-3), TM (transmembrane domain), and cyto (cytoplasmic domain). The splice variant in which exon 6 is skipped as indicated and leading to a premature stop is predicted according to the homologous experimentally established mouse transcript. The resultant isoGFRAL lacks D3 and the downstream transmembrane domain and could function as a soluble GFRAL receptor isoform. B: Schema depicting GDF15, full-length GFRAL, the putative splice variant isoGFRAL, and RET. RET domains are labelled CLD1-4 (Cadherin-Like), CRD (cysteine rich), TM (trans membrane), and KIN (kinase). The activated (phosphorylated) receptor complex GDF15-GFRAL-RET is shown in the middle, while the putative isoGFRAL receptor is depicted extracellularly bound to GDF15. C: CryoEM structure of GDF15-GFRAL-RET ectodomain (PDB access code 6Q2J, surface visualization). The 2 GDF15 molecules in the dimer are distinguished in different shades of blue. Arrows indicate the linkers to the membrane for RET (left) and GFRAL (right) to the membrane (the remaining 2 are at the rear side).