Fig. 7. Robustness of the strain rate–dependent behavior and the scalability of the bi-beams.
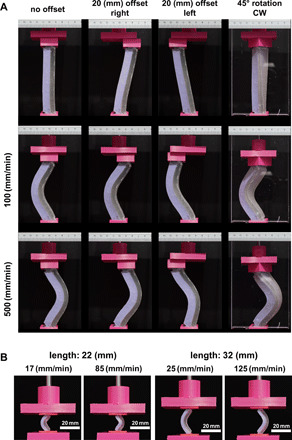
(A) The bi-beams (thick bi-beam, aspect ratio of 6, similar to those used in Fig. 4B) exhibited the same strain rate–dependent buckling behavior despite imperfect loading conditions, including 20-mm offsets to the left and right and ≈45° rotation in the bi-beams. (B) Two miniaturized bi-beams (left: length = 22 mm, aspect ratio = 3.7, and thickness = 10 mm; right: length = 32 mm, aspect ratio = 5.3, and thickness = 10 mm) were manufactured and tested under low and high loading speeds that were scaled with the length of the bi-beams so as to maintain the same approximate strain rates as was used in the previous experiments (i.e., Figs. 4 to 6). Scaling down the length of the bi-beams by up to ≈5.3 times did not change the strain rate–dependent buckling behavior of the bi-beams. Photo credit: Shahram Janbaz, Delft University of Technology.
