Figure 2.
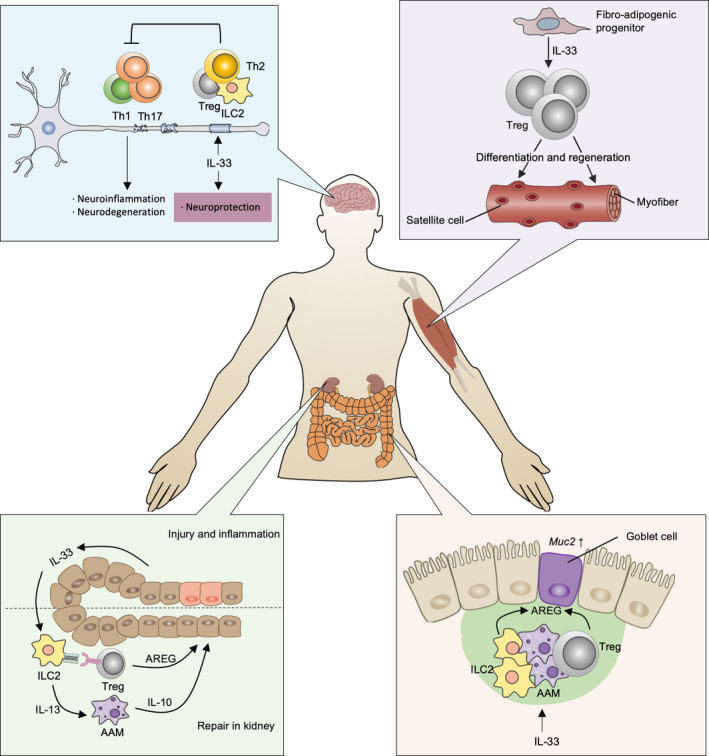
The action modes of IL‐33 during tissue repair and regeneration. IL‐33 confers neuroprotection by stimulating ILC2s and promoting Th2 and Treg accumulation, thereby reversing the pathogenic Th1/Th17 response. Furthermore, IL‐33 activates ILC2s and maintains a type 2 immune environment. These cytokines subsequently induce broad anti‐inflammatory immune cells, such as AAMs and Tregs, that produce IL‐10 and AREG. As a result, the levels of inflammation in the kidney are downgraded and IL‐33 rescues kidney function. In addition, IL‐33 is also important for the regeneration of muscle tissue. It can direct the differentiation and the regeneration of myofibers and satellite cells through Treg expansion. Successful mucosal healing is often achieved by the expression of Muc in response to IL‐33, which is present in AREG‐derived ILC2s and Tregs.
