FIGURE 2.
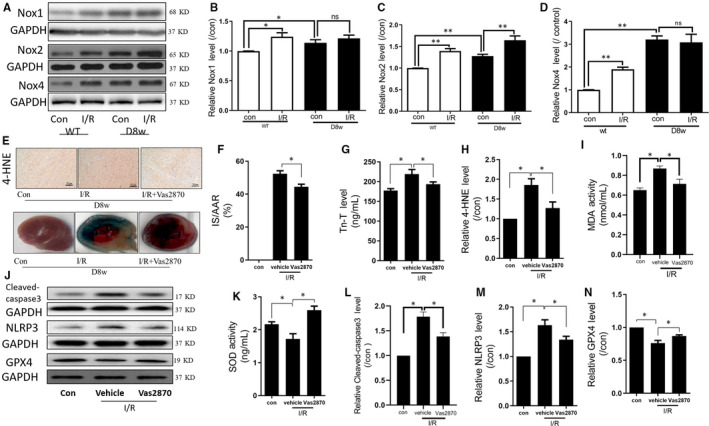
Nox inhibition attenuates post‐ischaemic programmed cell death and cardiac injury in diabetic rats. A, WB bands depicting the protein expression of Nox1, Nox2, Nox4 and GAPDH; B, The change in the protein expression of Nox1 in Con and diabetic rats; C, The change in protein expression of Nox2 in Con and diabetic rats; D, The change in protein expression of Nox4 in Con and diabetic rats; E, 4‐HNE and TTC staining; F, The change of IS in response to treatment with or without Vas2870 in diabetic rats; G, Tn‐T release during myocardial I/RI in response to treatment with or without Vas2870 in diabetic rats; H, The relative 4‐HNE levels during myocardial I/RI in diabetic rats, with or without Vas2870 treatment; I, MDA release during myocardial I/RI in diabetic rats, with or without Vas2870 treatment; J, WB bands depicting protein expression of cleaved caspase‐3, NLRP3 and GPX4; K, SOD release during myocardial I/RI in diabetic rats, with or without Vas2870 treatment; L, The change in the protein expression of cleaved caspase‐3 during myocardial I/RI in diabetic rats, with or without Vas2870 treatment; M, The change in the protein expression of NLRP3 during myocardial I/RI in diabetic rats, with or without Vas2870 treatment; N, The change in protein expression of GPX4 during myocardial I/RI in diabetic rats, with or without VAS2870 treatment. Myocardial ischaemia reperfusion(I/R) was achieved by 30 min ischaemia and 120 min reperfusion. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 6 per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01
