FIGURE 3.
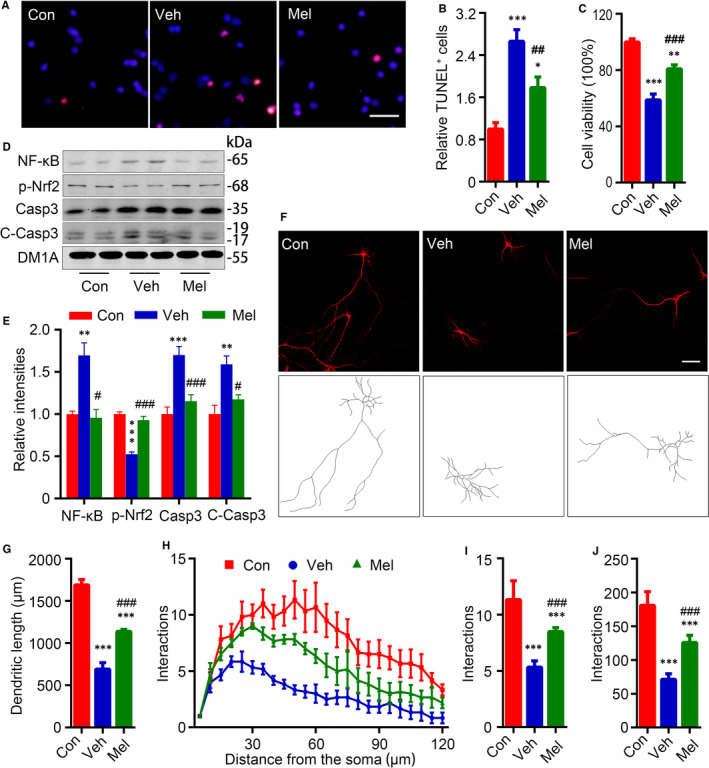
Melatonin impeded neuronal apoptosis and dendritic abnormalities in acidic condition. A, Neurons were treated with melatonin (Mel) (1 × 10−4 mol/L, Mel) or DMSO (0.01%, Veh) for 24 h, and TUNEL staining and CCK8 were performed to validate the cell death ratio and cell viability after pH6.2 for 24 h. TUNEL staining was performed after pH6.2 treatment for 24 h (Scale bar = 50 μm) and quantified (B). Data were presented as means ± SEM (n = 4/group). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 vs Con, ## P < 0.01 vs Veh. C, The relative cell viabilities of rat cortical neurons after pH6.2 for 24 h were shown. Data were presented as means ± SEM (n = 6/group). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs Con, ### P < 0.001 vs Veh. Levels of nuclear factor κ‐light‐chain‐enhancer of activated B cells (NF‐κB) p65, phosphorylated nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (Nrf2) at Ser40 (p‐Nrf2), caspase‐3 (Casp3) and cleaved caspase‐3 (C‐Casp3) were measured by Western blotting (D) and quantitatively analysed (E). Data were presented as means ± SEM (n = 4/group). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs Con, # P < 0.05, ### P < 0.001 vs Veh. F, Representative images for observing neurons were showed after MAP2 staining (Scale bar = 50 μm). G, Total dendritic length was quantified using the software ImageJ loaded with the simple neurite tracer analysis plug‐in. H, Neuronal dendritic complexity was analysed using ImageJ software and Sholl analysis plug‐in, and maximum number of dendritic intersections (I) and sum of total dendritic intersections (J) were quantified. Data were presented as means ± SEM (n = 6/group). ***P < 0.001 vs Con, ### P < 0.001 vs Veh
