FIGURE 8.
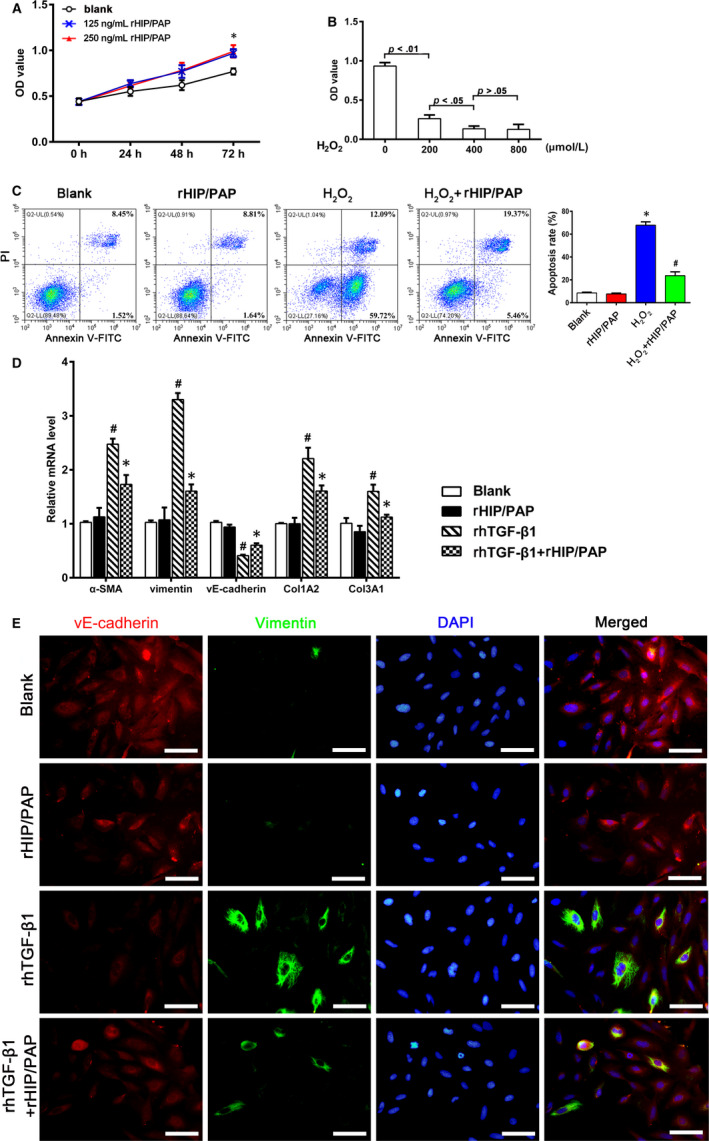
HIP/PAP accelerates proliferation, alleviates H2O2‐induced apoptosis, and inhibits TGF‐β1‐induced EndoMT in HPMVEC. rHIP/PAP at 125 and 250 ng/mL promoted HPMVEC growth to similar extents. * P < 0.05 vs the blank control (A). H2O2 treatment suppressed HPMVEC viability in a concentration‐dependent manner over the range of 0 ‐ 400 μM (B). Flow cytometry analysis revealed that rHIP/PAP (125 ng/mL) protects HPMVEC from H2O2‐induced (200 μM) apoptosis. * P < 0.01 vs the blank or rHIP/PAP group, # P < 0.05 vs the H2O2 group (C). rhTGF‐β1 (5 ng/mL) increased α‐SMA, vimentin, Col1A2, and Col3A1 expression and decreased vE‐cadherin expression in HPMVEC, while rHIP/PAP (125 ng/mL) markedly attenuated these alterations without affecting their basal expression (D, E). This suggests an antagonizing effect of HIP/PAP on the TGF‐β1‐induced EndoMT. # P < 0.01 vs the blank or rHIP/PAP group, * P < 0.05 vs the rhTGF‐β1 group. Error bars indicate SD. Scale bars = 50 μm
