Figure 5:
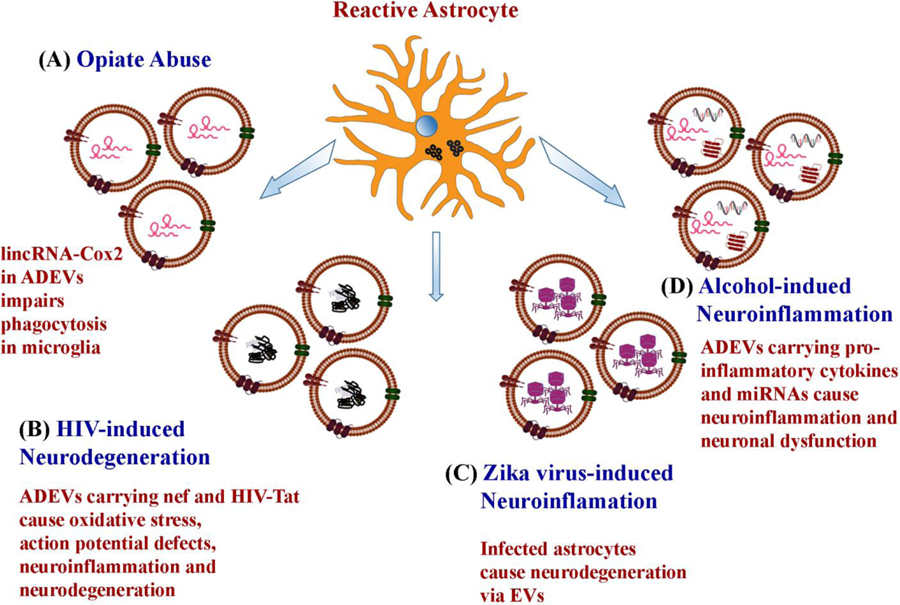
Potential mechanisms by which astrocyte-derived EVs (ADEVs) mediate neurotoxicity in opiate abuse, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)- and Zika virus-induced neurodegeneration, and alcohol intake-induced neuroinflammation. Opiates such as morphine upregulate long intergenic noncoding RNA lincRNA-Cox2 in ADEVs, which impairs the phagocytic behavior of microglia when internalized. In HIV associated neurological disorder, ADEVs carry an HIV associated protein negative regulator factor (nef) and HIV-1 transactivator of transcription (HIV-Tat), which cause increased oxidative stress, reduced neurite and axonal growth, impaired action potential and neurodegeneration by inducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and other toxic proteins. In Zika virus infection, astrocytes get infected first and promote neurodegeneration through EVs secreted by them. In alcohol-induced neuroinflammation, EVs secreted by alcohol-exposed astrocytes carry pro-inflammatory cytokines and miRNAs, which cause neuroinflammation and neuronal dysfunction.
