Fig. 2.
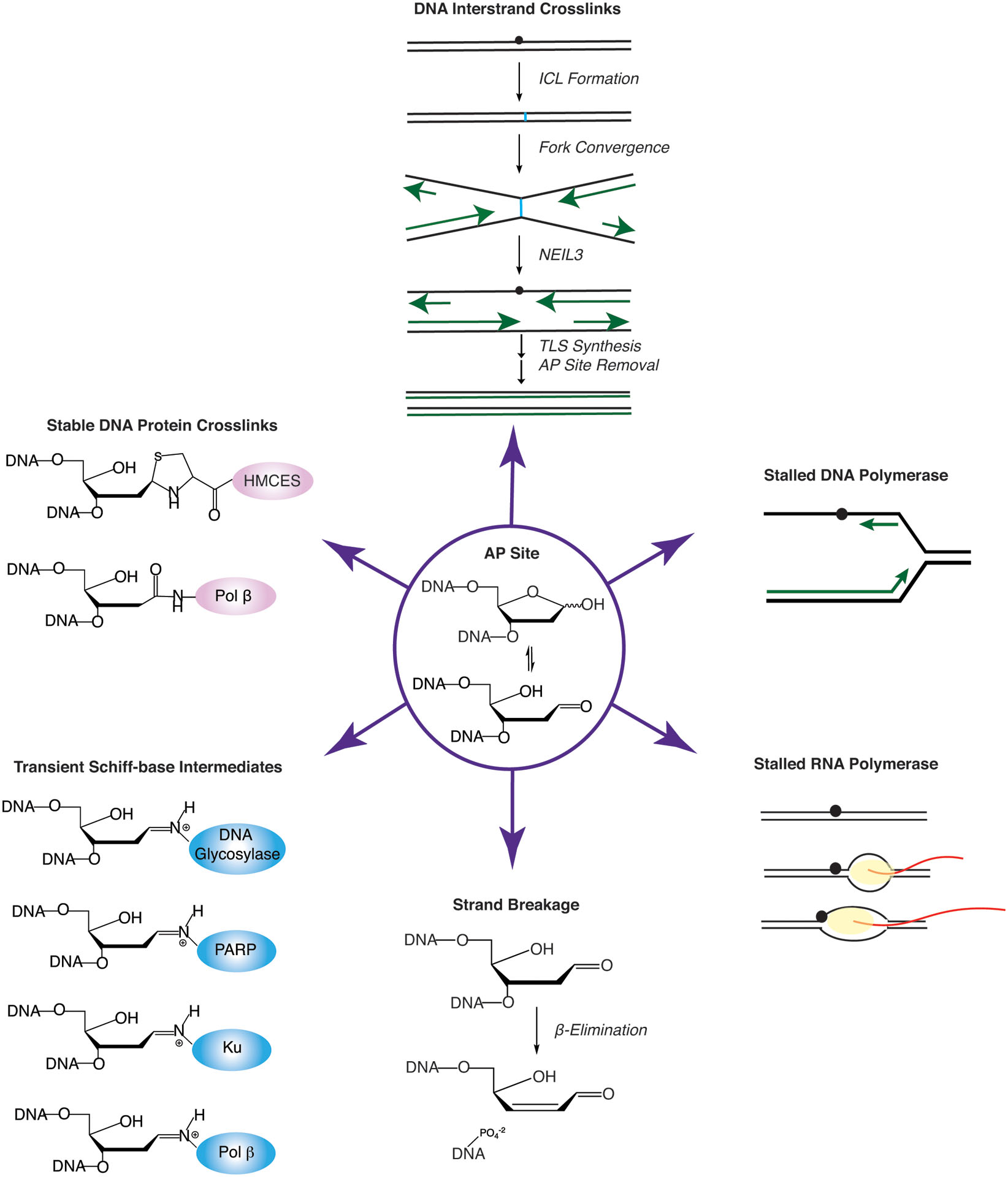
Consequences of unrepaired AP sites. AP sites (in center) react to form stable (pink) or transient (blue) DNA-protein crosslinks (DPCs) (left), generate intrastrand crosslinks (ICLs) (top), stall DNA polymerases and RNA polymerases (right), and can cause strand breakage via β-elimination (bottom).
