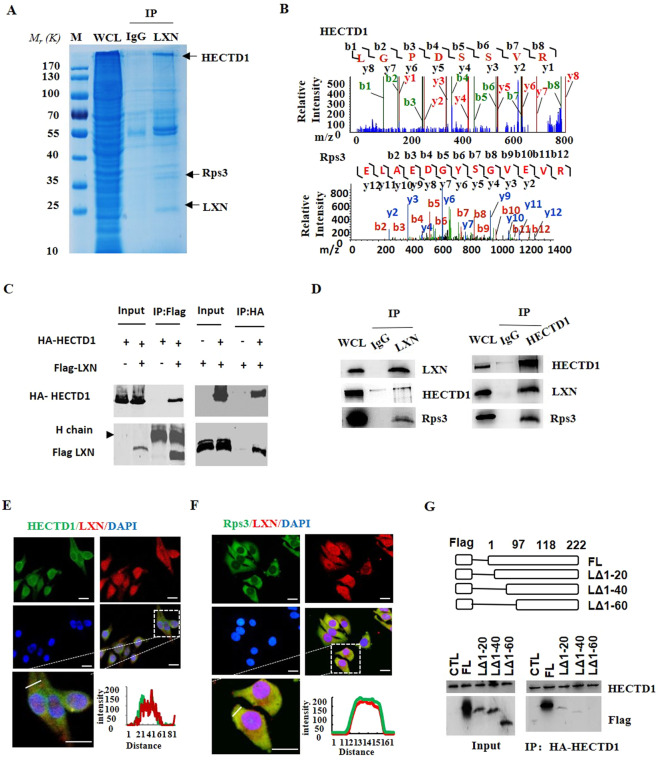
Figure 4.
LXN forms a complex with HECTD1 and Rps3 in HIEC cell. (A,B) Cell lysates from HIEC cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-LXN antibody or control IgG, and then the purified protein complex was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and stained with coomassie brilliant blue (A), the differential bands were cut and in-gel digested with trypsin. Peptides were subject to LC-MALDI MS/MS assay. Identified peptide and MS/MS spectrum that matched with the sequence of HECTD1 and Rps3 are shown (B). (C) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with HA-HECTD1 and Flag-LXN plasmids. 48 h after co-transfection, immunoprecipitation was performed with either anti-Flag antibody or anti-HA antibody to detect the interaction of HECTD1 with LXN. (D) Cell lysates obtained from HIEC cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-LXN, anti-HECTD1 antibody, respectively, IgG as control antibody, and then separated by 10% SDS-PAGE. Transferred membrane was immunoblotted with antibodies as indicated. (E,F) HCT116 cells were cultured in 6-well plates. The localization of HECTD1 and LXN (E), Rps3 and LXN (F) were analyzed by immunofluorescence staining with HECTD1, Rps3 and LXN antibody. Higher magnification inserts show details of localization. The pixel intensity of localization in the selected regions (white line) are shown. Scale bars = 10 μm. (G) HA-HECTD1 expression vector in combination with either empty vector or expression vectors of Flag-LXN mutants were co-transfected into HEK293T cells. Extracted proteins were precipitated by anti-HA antibody, and then separated by 10% SDS-PAGE. The transferred membrane was immunoblotted with either anti-Flag or anti-HA antibody.