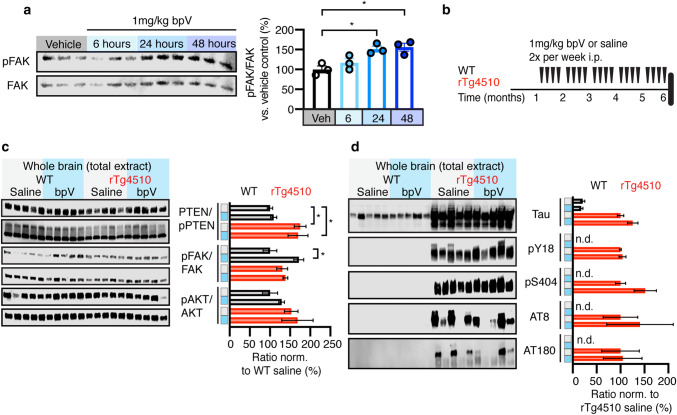
Fig. 6.
PTEN inhibition with bpV alters protein phosphatase pathway without reducing Tau levels or phosphorylation. a Representative western blots and quantification of pY397 FAK and total FAK in 6 month-old WT mice 6, 24, and 48 h after injection with bpV or saline control. b Study design of PTEN inhibition with bpV, injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) twice weekly for 5 months (starting at 1 month of age). c Representative western blots and quantification of pPTEN relative to PTEN, pY397 FAK relative to total FAK, and pS473 AKT relative to total AKT in brain lysates from saline- or bpV-treated rTg4510 and WT mice. The quantified ratio is expressed as a percent normalized to the saline-treated WT group. c Representative western blots and quantification of total Tau relative to total protein and pY18, pS404, pS202/T205 and pT231 each relative to total Tau in brain lysates from saline- or bpV-treated rTg4510 and WT mice. The quantified ratio is expressed as a percent normalized to the saline-treated rTg4510 group. Data presented as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test, b, c two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test