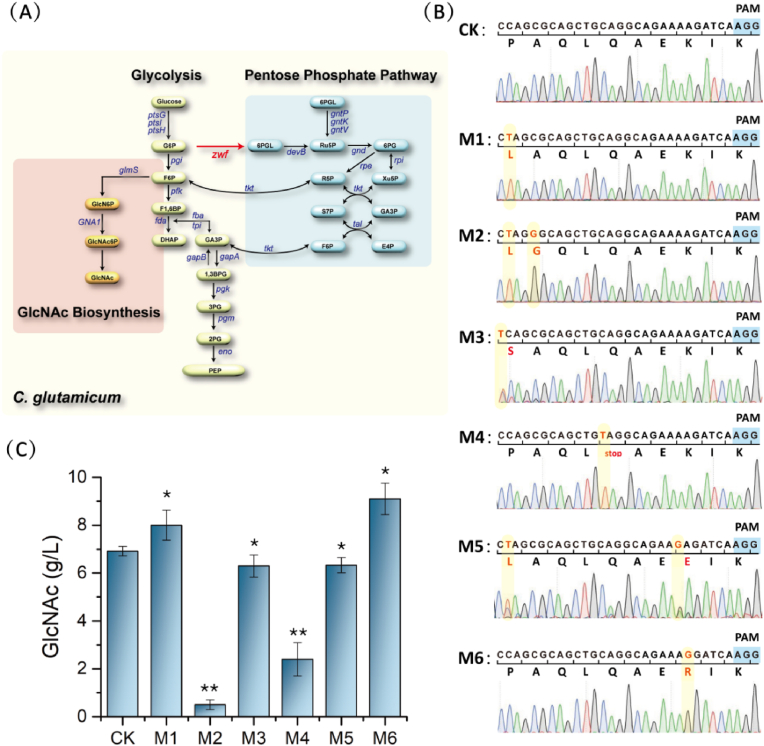
Fig. 5.
The zwf gene in the C. glutamicum S9114 strain was modified using base editing strategy. (A) Synthetic pathway of GlcNAc in C. glutamicum. The zwf gene is highlighted in red, and the pentose phosphate pathway linked by the gene is highlighted by blue square. (B) 6 mutant strains generated by single-base editing of zwf using the Ptac-TadA-dCas9-AID expression cassette. The mutated bases are highlighted by red letters, and the PAM sequences are highlighted by blue squares. Among them, the M4 strain produced a premature stop codon in zwf. (C) GlcNAc titer in 6 single-mutant strains. All data were the average of three independent studies with standard deviations. All data were expressed as mean ± SD. Differences were determined by 2-tailed Student’s t-test between two groups, or one-way. ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey’s test for multiple groups. Statistical significance is indicated as ∗ for p < 0.05 and ∗∗ for p < 0.01 relative to control strain S9114 ΔnagA-ΔgamA-Δldh, respectively. . (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)