Figure 1.
Dynamic Microtubule Changes Took Place at the Fzd Side of the Cell Cortex to Modulate BB Positioning at Ependymal Cells
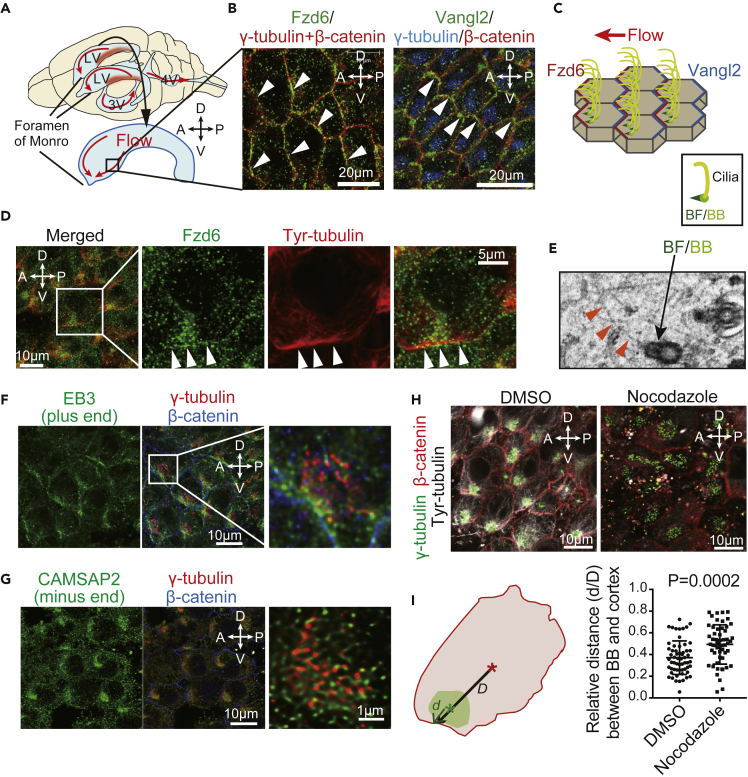
(A) Illustration of directional CSF flow in the brain ventricles. CSF (red arrow) is produced at the choroid plexus (red area) in the posterior region of the lateral ventricle (LV) and outflows through the Foremen of Monro at the anterior-ventral region of the LV, toward the third ventricle (3V) and fourth ventricle (4V). The illustration below represents the surface of a dissected right distal LV wall. Microscopy images of the boxed area are shown for all experiments. A, anterior; P, posterior; D, dorsal; V, ventral sides of the brain.
(B) Confocal images of the LV wall at the horizontal plane show the apical cell cortex of ependymal cells. Whole mounts of LV wall tissue were stained with antibodies against Fzd6 (left panel, green), Vangl2 (right panel, green), γ-tubulin (basal bodies, red in the left panel or blue in the right panel), and β-catenin (cell boundary, red). Arrowheads indicate asymmetric localization of Fzd6 at the anterior-ventral side (left panel) or Vangl2 at the posterior-dorsal side (right panel) of the apical cell membrane of ependymal cells.
(C) Representation of ependymal cells lining the LV wall, the orientation of multiple cilia (yellow), and asymmetric localization of Fzd6 (red) and Vangl2 (blue) at the apical cell membrane, parallel to surface CSF flow (red arrow). BF (basal foot, green) and BB (basal body, light green) located at the base of cilia are rotationally oriented toward the Fzd side.
(D) Whole-mount staining of the LV wall with antibodies against Fzd6 (green) and tyrosinated (Tyr)-tubulin (red). Arrowheads indicate sites of Fzd6 accumulation with tyrosinated tubulin located at the ventral side of the apical cell membrane.
(E) Image of an ependymal cell at the LV wall obtained by electron microscopy shows filaments (arrowheads) connected to the BF/BB structure.
(F) Whole-mount staining of the LV wall with antibodies against EB3 that marks the microtubule plus end (green), γ-tubulin (red), and β-catenin (blue).
(G) Whole-mount staining of the LV wall with antibodies against CAMSAP2 that marks the microtubule minus end (green), γ-tubulin (red), and β-catenin (blue) antibodies.
(H) Tissue explants from the LV wall were incubated with DMSO or Nocodazole (10 μM) for 24 h and stained with antibodies against tyrosinated tubulin (white), γ-tubulin (green), and β-catenin (red).
(I) Illustration (left) shows the measurement of the distance between the cell cortex and the center of the BB cluster (d) or the cell surface (D). The ratio of d/D was represented as the relative distance between the BB cluster and the cell cortex. Quantification (right) is represented as the mean ± SEM of 54 cells from three mice in each treatment group (representative microscopy data shown in [H]). Data are represented for d/D with DMSO and Nocodazole treatment.