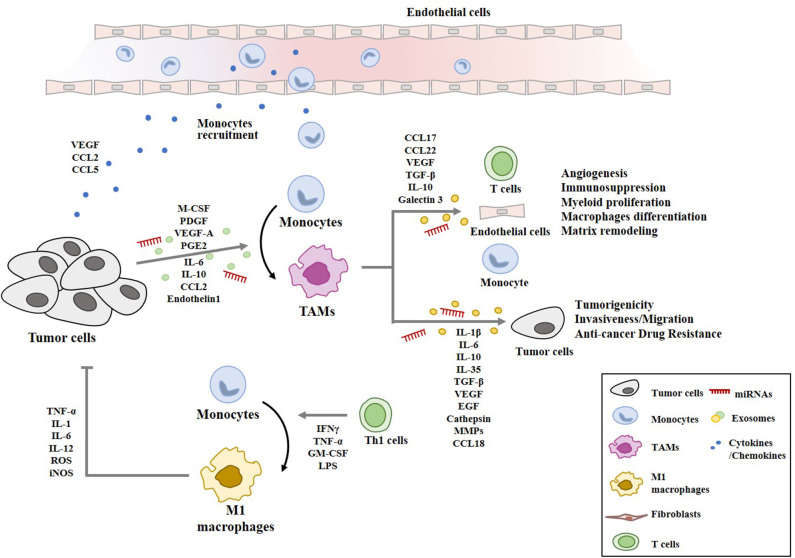
Figure 3.
Cellular interactions involving macrophages in tumor microenvironment. Cancer cells secrete chemoattractants and growth factors (CCL2, CCL5, VEGF, M-CSF) to recruit blood monocytes. Tumor-derived M-CSF, PDGF, IL-6, IL-10, TGF-β, VEGF-A, CCL2, PGE2, and endothelin 1 induce the polarization into M2-like macrophages with pro-tumor functions (TAMs). TAMs-derived cytokines/growth factors (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-35, TGF-β, VEGF, and EGF), cathepsin, and MMPs enhance tumor cell proliferation, invasion, anti-cancer drug-resistance, and remodeling of extracellular matrix. TAMs-derived chemokines (CCL17, CCL18, and CCL22) recruit naïve and Th2 lymphocytes, which results in ineffective anti-tumor immune response. miRNAs denote microRNAs. M1 macrophages are activated by Th1 cells. M1 macrophages display anti-tumoral functions through TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, ROS, and iNOS.