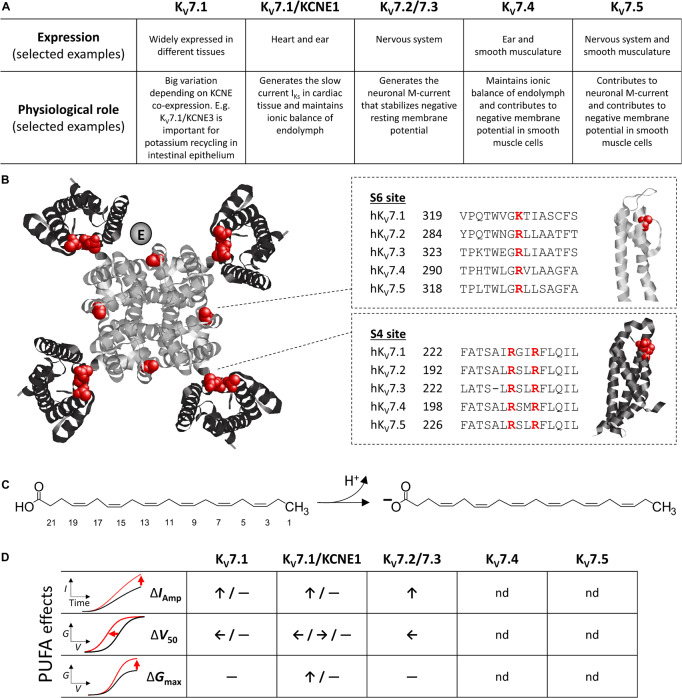
FIGURE 1.
Overview of KV7 channel and PUFA molecular structures, and typified PUFA effects. (A) Schematic overview of KV7 subtype expression and functional role. Note that these are examples, as some KV7 subtypes have widespread expression and function. (B) Top view of KV7.1 (PDB: 5VMS) with central pore domain in gray and peripheral voltage-sensing domains in black. Putative localization of KCNE at one KV7.1 channel subunit is indicated [each subunit may accommodate one KCNE subunit (Sun and MacKinnon, 2020)]. Experimentally identified positively charged residues important for PUFA effects in KV7.1 (Liin et al., 2018) are highlighted in red. Sequence alignment of the S6 site (important for Gmax effect) and S4 site (important for V50 effect) of all KV7 isoforms are provided along with a side view of relevant channel domain. (C) Structure of the PUFA DHA, which has a carboxyl head linked to a 22-carbon long aliphatic tail with six cis double bonds. Deprotonation of the carboxyl head occurs at pH exceeding the pKa of the head-group, this endows DHA with a single negative charge. (D) Schematic overview of PUFA effect on current amplitude (IAmp), mid-point of the G(V) curve (V50), and maximum conductance (Gmax) on indicated KV7 subtypes. Please refer to Table 1 for further details. nd denotes not determined.