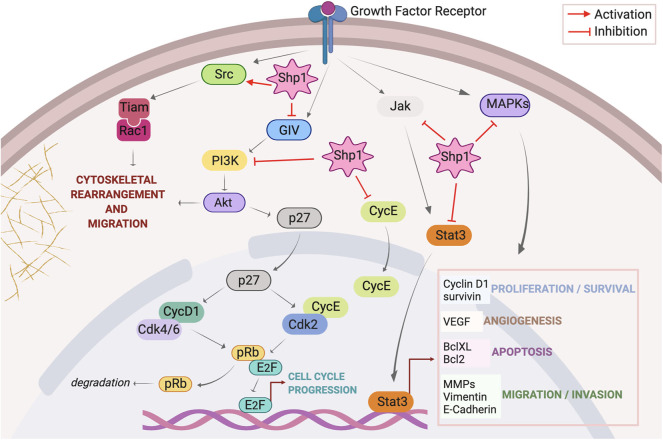
Figure 1.
Overview of signaling pathways regulated by Shp1. Activation of growth factor receptors initiates signaling through Src, PI3K/Akt, JAK/STAT, and MAPKs axes. Once activated Src triggers a signal pathway that culminates with the assembly of Tiam/Rac1 complex at the plasma membrane and consequent formation of peripheral ruffles with stimulation of cell motility; Shp1 dephosphorylates Src on the inhibitory pTyr527 thus activating this cascade. Membrane receptor activation triggers the tyrosine phosphorylation of GIV that directly binds and activates PI3K; this in turn activates Akt inducing cytoskeletal rearrangements. Shp1 dephosphorylates GIV and inhibits Akt activation via the GIV-PI3K axis. Akt also phosphorylates p27(kip1) (p27) at Thr157, promoting its cytoplasmic localization and abolishing its inhibitory effect on cell cycle components like cyclin D1-Cdk 4/6 and cyclin E-Cdk 2 complexes; this results in increased pRb phosphorylation and dissociation from E2F, stimulation of transcriptional activity with consequent cell cycle progression. Shp1 blocks p27(kip1) nuclear localization through the regulation of PI3K/Akt activity. Shp1 also controls cell cycle progression regulating cyclin E localization. Following receptor stimulation, activated JAK phosphorylates STAT3, resulting in the translocation of activated STAT3 (p-STAT3) to the nucleus; Shp1 can directly dephosphorylate STAT3 or its upstream JAK thereby hampering STAT3-regulated cellular proliferation and survival, angiogenesis, apoptosis, migration, and invasion. Finally, Shp1 is involved in the attenuation of growth factors induced cell proliferation trough inhibition of MAPKs pathway.