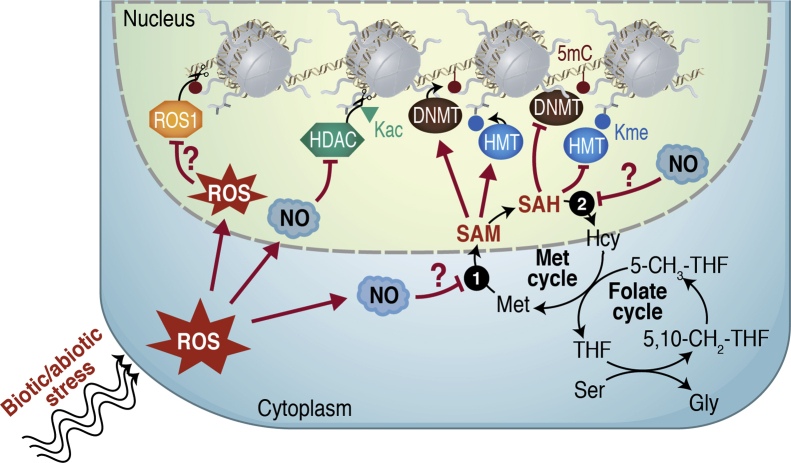
Figure 2.
Model of stress interactions of metabolism and chromatin modification. Environmental stress leads to increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and NO. ROS may lead to inactivation of DNA glycosylases involved in DNA demethylation (for example, ROS1). NO acts as an HDAC inhibitor and may also affect the activity of enzymes in the methionine (Met) cycle, for example, SAMS4 (1) and SAHH1 (2), leading to changes in SAM and SAH levels. This can lead to changes in histone lysine methylation (Kme) and cytosine methylation (5mC), as DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and histone methyltransferases (HMTs) require SAM as methyl donor and are inhibited by SAH. The Met cycle depends on C1 supply from the folate cycle.