Figure 3.
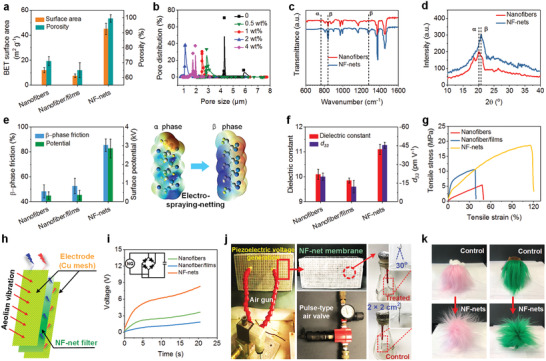
a,e–g,i) Comparison of: a) BET surface areas and porosities, e) β‐phase frictions, f) dielectric constants and d 33 values, g) tensile stresses, and i) piezoelectric charging performances between PVDF nanofiber, nanofiber/film, and NF‐net membranes. i) Inset: A schematic of a circuit diagram for capacitor charging of the nanogenerator. b) Pore size distribution of the PVDF NF‐net membranes obtained from solutions with various DTAB concentrations. c) FTIR spectra and d) XRD patterns of PVDF nanofiber and NF‐net membranes. h) Schematic diagram of the self‐charging nanogenerator based on PVDF NF‐nets. j) A set of photographs showing the piezoelectric voltage generation of window screens using PVDF NF‐net filters due to pulse‐type airflow. The electroscope confirms an obvious charging process of SWING filters due to wind pressure. k) Snapshot images of fluffy toys sitting on the PVDF control nanofiber and SWING filter membranes treated by pulse‐type airflow (20 min).
