FIGURE 2.
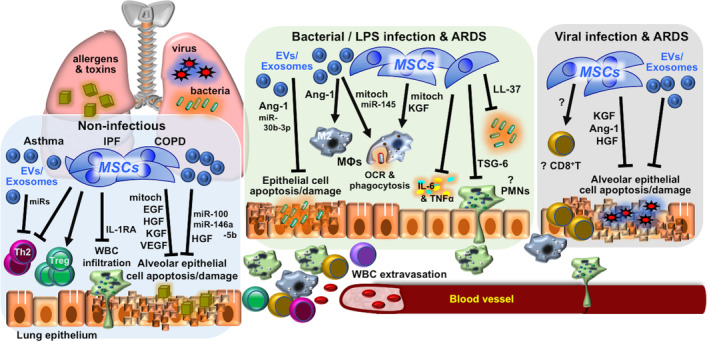
Mechanisms involved in MSC therapy for immune/inflammatory pulmonary disorders. Mechanisms reported in in vivo preclinical studies of MSC therapy for immune/inflammatory lung diseases of non‐infectious etiology—including asthma, IPF, and COPDs—and infectious etiology—including bacterial and/or LPS and viral infection and related ARDS. Detailed descriptions can be found in the text. Ang‐1, angiopoietin‐1; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; COPD, chronic obstructive lung disease; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EV, extracellular vesicles; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IL‐1RA, interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist; IPF, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; KGF, keratinocyte growth factor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MΦ, macrophage; miRs, microRNAs; mitoch, mitochondria; MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; OCR, oxygen consumption rate; PMNs, polymorphonuclear leukocytes/neutrophils; Th2, T helper type 2 lymphocytes; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor‐α; Treg, regulatory T lymphocytes; TSF‐6, TNF‐stimulated gene 6 protein; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; WBCs, white blood cells
