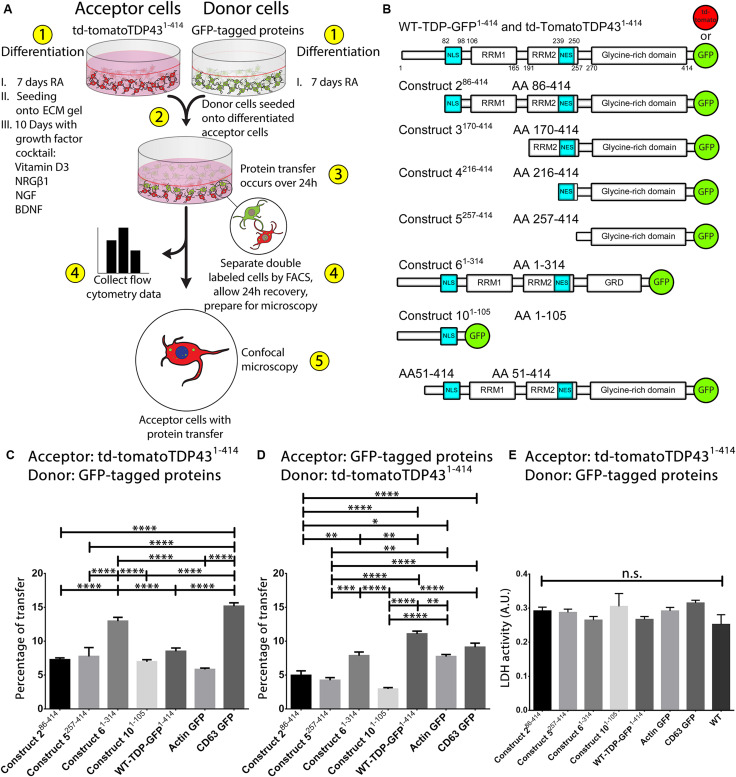
FIGURE 1.
Preservation of the N-terminus of TDP-43 promotes its transmissibility between cells. A visualization of the coculture model is provided in (A). Cells are differentiated in ECM gel with growth factors according to the scheme described in (A) prior to formation of the coculture. After 24 h of coculture, cells are analyzed and separated using FACS and prepared for microscopy. Experiments involve the use of full-length TDP-43 and TDP-43 truncated fragments, all of which are fused to fluorescent proteins at the C-terminus (B). Two full-length TDP-43 proteins were used, td-tomatoTDP431– 414 and WT-TDP431– 414 (GFP), whereas all TDP-43 protein fragments were fused with EGFP. All fragments of TDP-43 transferred directly from donor cells (GFP) to td-tomatoTDP431– 414 acceptor cells with differing degrees of efficiency (C). Full-length td-tomatoTDP431– 414 donor cells transferred protein at similar levels to TDP-43 fragment expressing acceptor cells (D). Construct 61– 314 was transferred most readily among the different TDP-43 fragments, indicating that preservation of the N-terminus (and/or loss of the extreme C-terminus) of TDP-43 is influential to the transmissibility of TDP-43 between cells. Cell toxicity, as measured by LDH release, indicated that the cocultures did not exhibit cytotoxicity over 24 h (E). Images corresponding to data set C can be found in Figure 2, whereas images from data set D are presented in Supplementary Figure S3. Full ANOVA tables are available in Supplementary Tables S3, S4. Data are presented as the proportion of all detected acceptor cells that are double labeled, provided as the mean ± SEM. Significance determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test, n = 6–10 (C), and n = 4–7 (D). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, n.s., not significant. BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; NRGβ1, neuregulin-β1; NGF, nerve growth factor; RA, retinoic acid; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; NLS, nuclear localization sequence; NES, nuclear export sequence; RRM, RNA recognition motif.