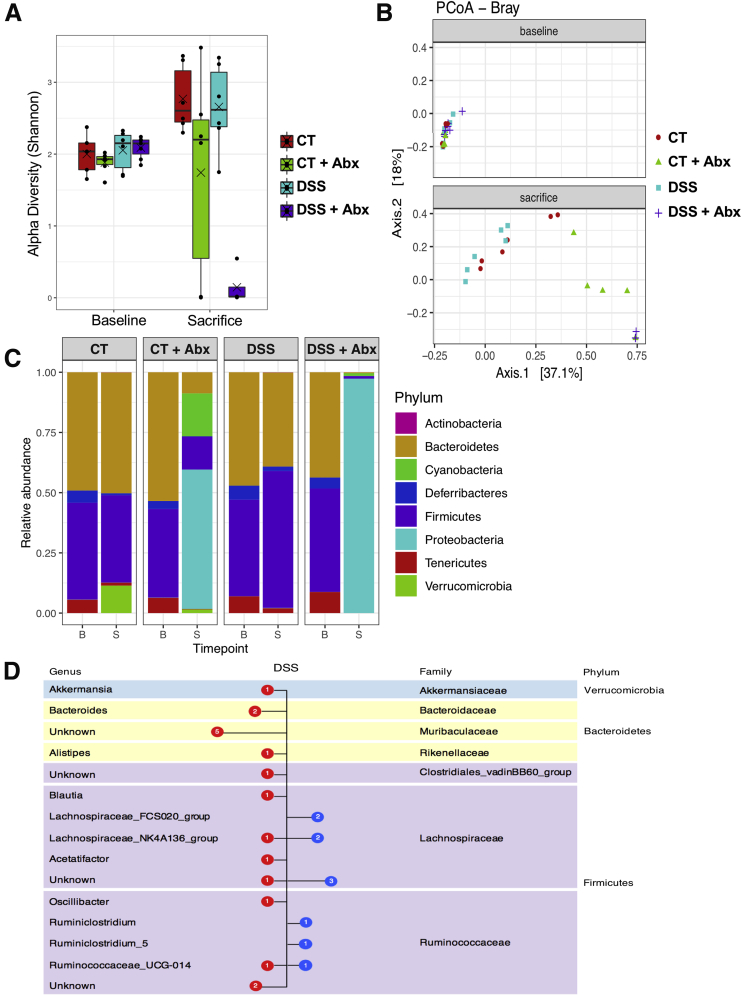
Figure 4.
Postinflammatory DSS mice exhibit changes in the microbiome. The alpha (A) and beta (B) diversity was assessed in controls, postinflammatory DSS, and antibiotic-treated mice. Baseline samples were not different; antibiotic treatment caused significant shifts in both alpha (linear mixed-effects model, P = .0072) and beta diversity (permutational multivariate analysis of variance, P < .001). Points represent individual samples, lines represent the median, and crosses represent the mean. (C) Relative abundance of different phyla at baseline (B) and sacrifice (S) time points. No significantly different phyla were seen at baseline between groups. (D) Comparison of bacterial content at the genus level between control and postinflammatory DSS mice at the sacrifice time point. Blue symbols represent families significantly increased in the postinflammatory DSS mice, and red symbols represent families significantly increased in controls (beta-binomial regression model, P <.01). N = 6/group, except DSS + Abx baseline, n = 7, control baseline, n = 5, and DSS + Abx group at sacrifice, n = 4. Abx, antibiotics; DSS, dextran sulfate sodium.